Wireless Society Realized by I-PEX in 2030
The following five goals for the wireless society in the 2030s need to be realized.
In order to realize these five goals of a radio-enabled society, a next-generation system that should be realized in the 2030s has been proposed.
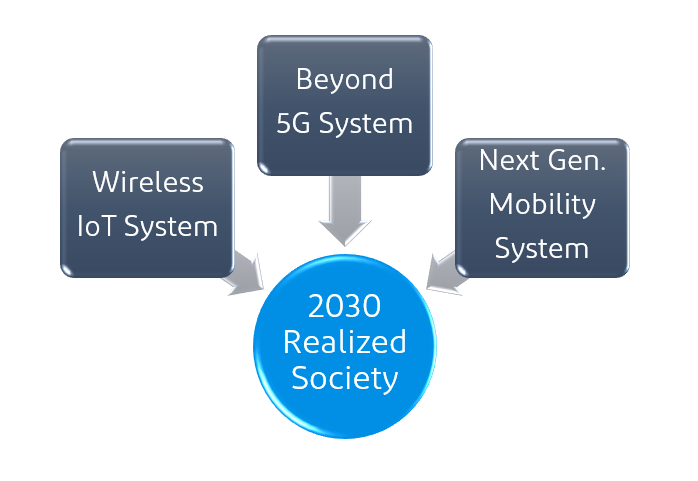
1.Beyond 5G System
① The need for super mass capability
It is believed that high-speed transmission using a wide frequency bandwidth is necessary to increase the capacity of next-generation mobile communications. For this purpose, it is proposed that it is necessary to secure frequency bands and develop technologies to enable the use of higher frequency bands such as millimeter wave and sub-terahertz wave (90 GHz~300 GHz).
② Establishment of high-frequency band communication technology
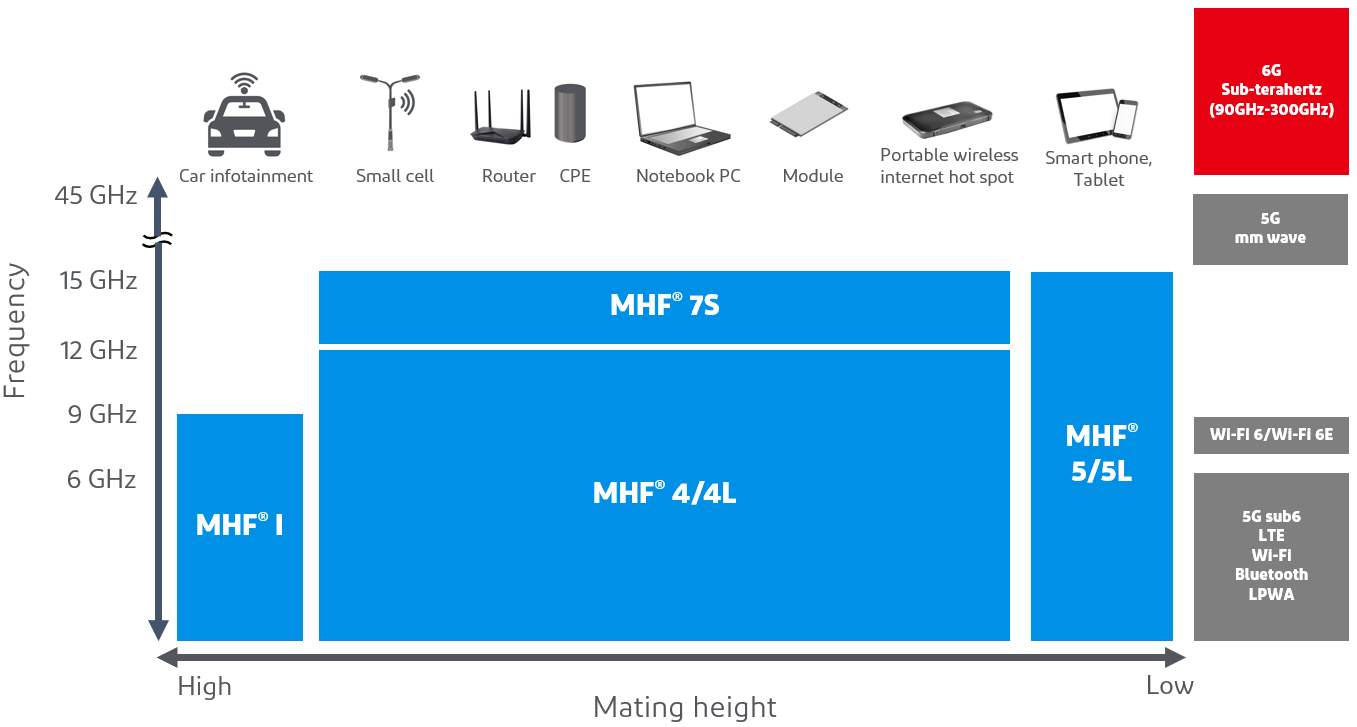
Fifth-generation mobile communication systems (5G) using the millimeter wave band are being put into practical use worldwide, and methods to achieve higher transmission speeds by using even higher frequencies have been proposed for next-generation and beyond mobile communication systems. To achieve this, it will be important to use a combination of lower frequency bands and millimeter wave bands in addition to sub-terahertz waves in 6G. To achieve this, technology is needed to use the existing frequency bands of 5G for 6G. This is a comparison of 4G, 5G, and currently considered 6G standards, as well as wireless LAN standards.
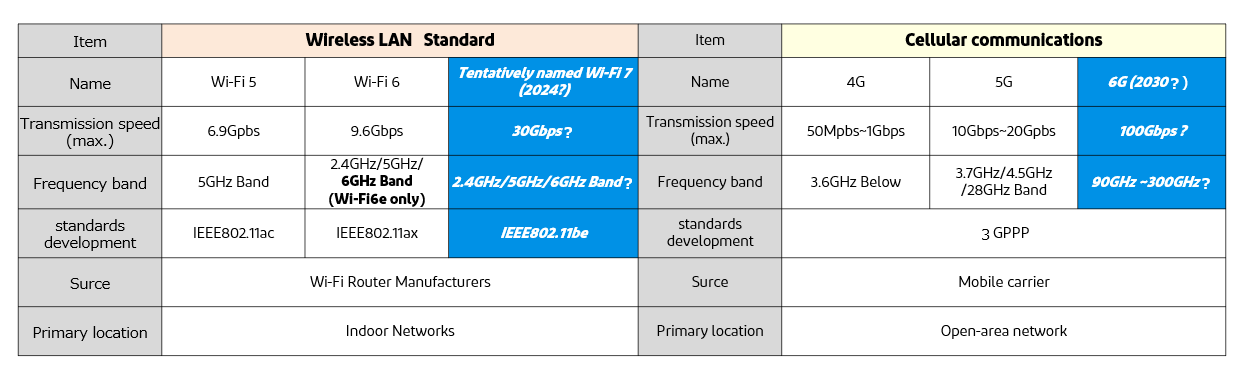
Currently, our products support up to 5G and Wi-Fi 6e frequency bands. Although the specific frequency band for 6G is not yet known, we are working to create products that satisfy the expected 6G standard.
Related article page: Beyond 5G System connectors
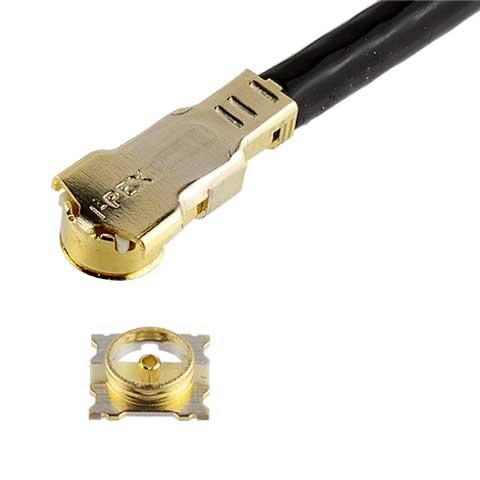

Excellent EMC performance with fully-shielded design, ideal for 5G mmWave applications, VSWR 1.5 max at 15 GHz in small 2.0 x 2.0 mm footprint |
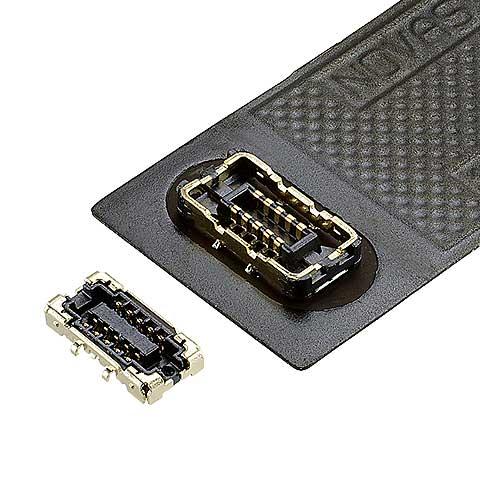

Ideal for 5G mmWave antenna module and devices, fully-shielded and narrow design, Power supply is available with Corson Alloy contact, 0.35 mm pitch, 0.7 mm height |
2. Wireless IoT System
Many wireless technologies, such as wireless LAN and 4G/5G, continue to evolve toward higher speeds, and in the IoT, there are cases where small sensor data, etc., must be sent over a long distance. LPWA (Low Power Wide Area-network) is the wireless technology to meet this demand.
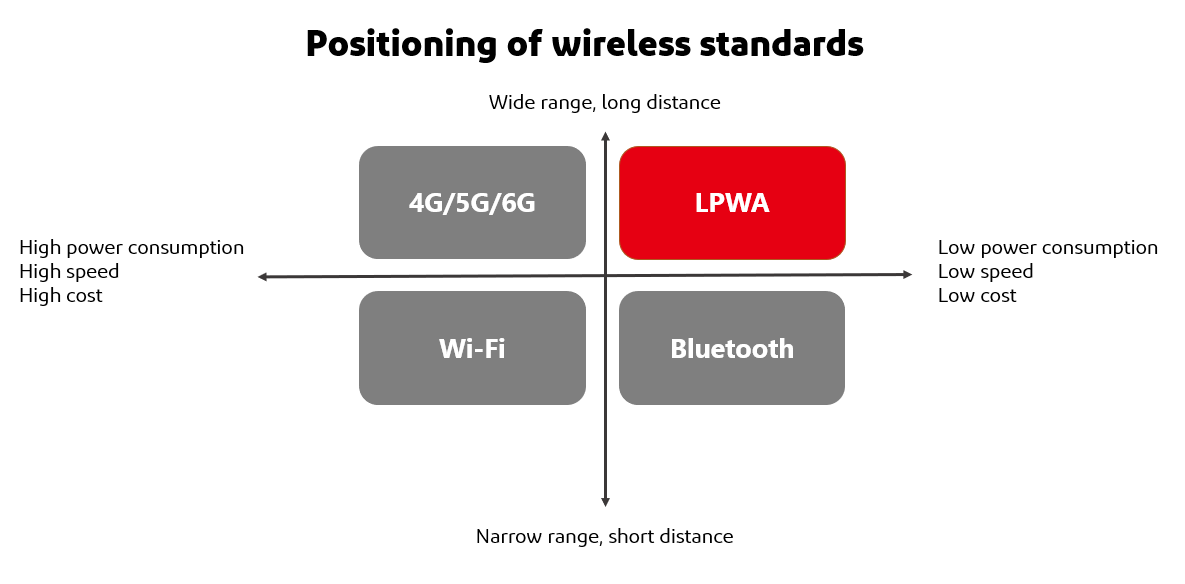
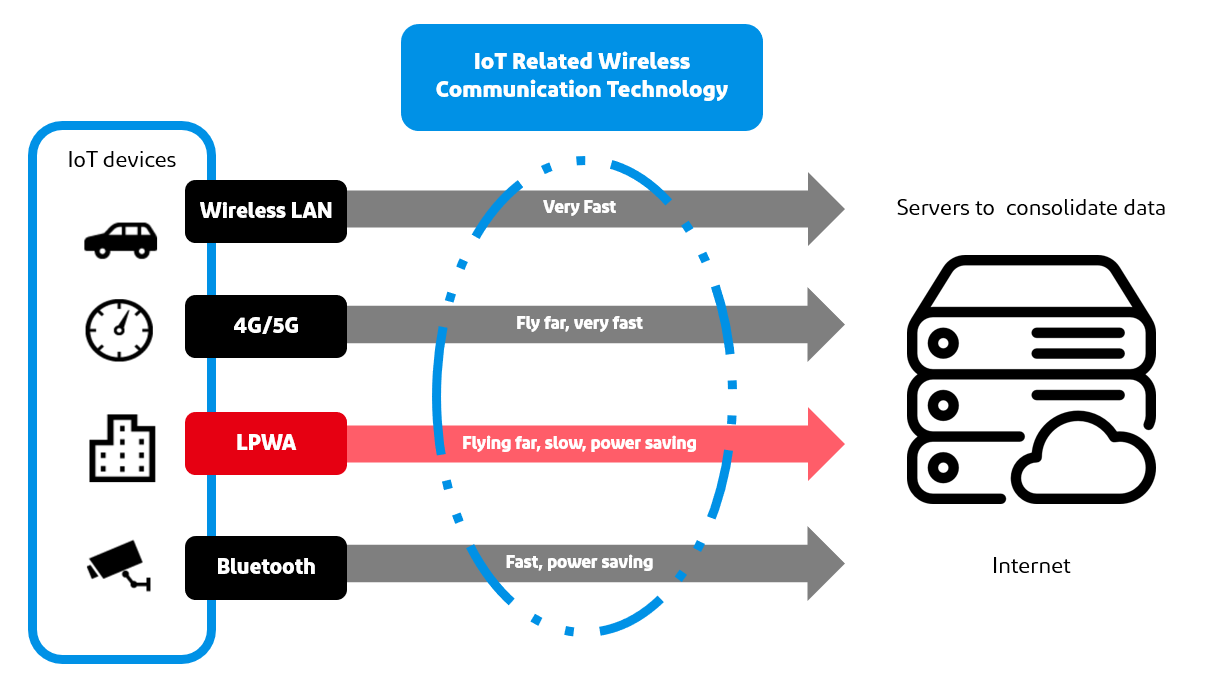
Currently, wireless communication systems for sensing include Wi-SUN, SigFox, and LoRaWAN as wireless communication systems that do not require a license, and NB-IoT and other standards as LPWA wireless communication systems that do require a license. Our products support not only the conventional 920 MHz band LPWA wireless communication method necessary to build wireless IoT systems, but also IEEE802.11ah (Wi-Fi HaLow), a network for the IoT that differs from conventional LPWA in that it can transmit images and video.
Related article page: Wireless IoT System connectors
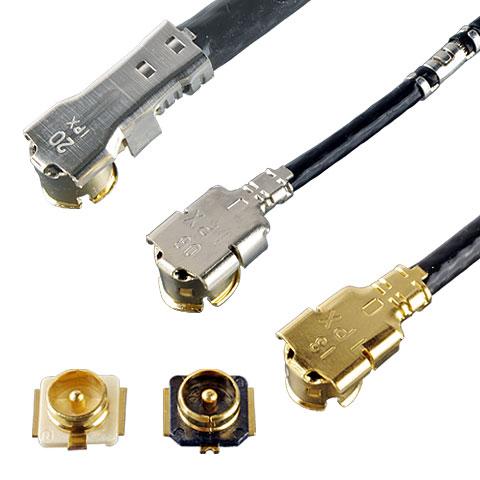

Supports up to 9 GHz, mated height of 2.5 mm max. and 3.0 mm max. |

The M.2 industry standard, mated height of 1.2 mm, 1.4 mm, and 1.7 mm max.,excellent electrical performance up to 12 GHz |
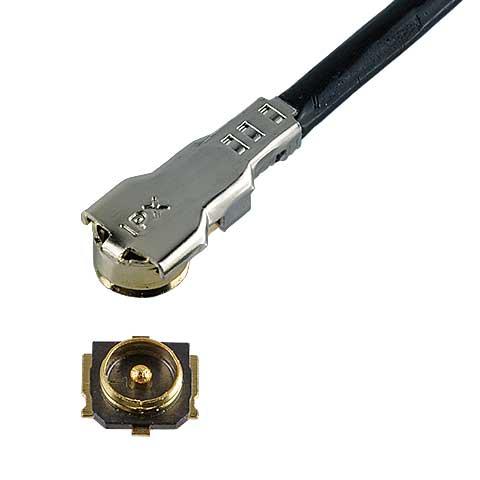

Improved electrical performance of 1.6 VSWR through 15 GHz,mated height of 1.3 mm max. |
3. Next Generation Mobility System
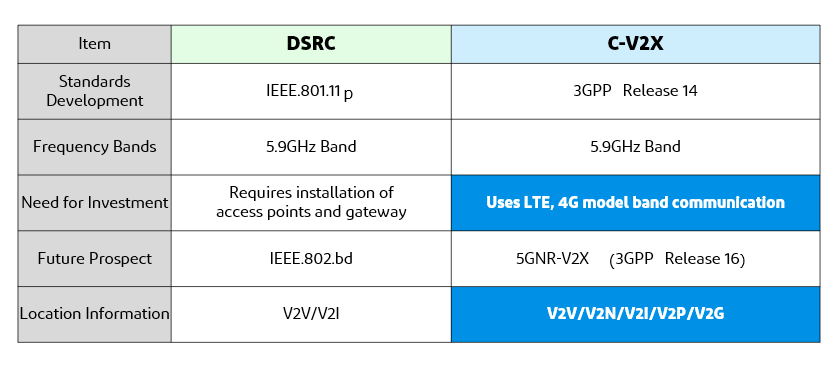
There are two standards for communication methods outside the vehicle (next-generation vehicle-to-vehicle and road-to-vehicle) to realize the connected car: dedicated narrowband communication (DSRC) and cellular V2X (C-V2X).
DSRC (Dedicated Short Range Communication)
DSRC is a communication technology based on wireless LAN technology, such as IEEE 802.11p (5.9 GHz band) and requires a new infrastructure.
C-V2X (Cellular Vehicle to Everything)
It is a mobile phone-based communication technology (Long-Term Evolution V2X (LTE-V2X)) standardized in 2016 by the 3rd Generation Partnership Project (3GPP). The standard uses the frequency band 5855 MHz~5925 MHz and is promoted by the 5GAA (5G Automotive Association).
Regarding next-generation inter-vehicle and roadside-to-vehicle communication technologies, the DSRC standard has already been put into practical use as a communication technology for ETC in Japan. However, DSRC needs to be upgraded to meet the communication demands of automobiles in the era of automated driving and cooperative driving. On the other hand, cellular V2X (C-V2X), a cellular communication system, is being developed into an NR-V2X communication system based on 5G technology in the future.
It is not yet clear whether DSRC or C-V2X will become the mainstream or how automotive communication technologies will be unified in the future, but our connectors are compatible with both DSRC and C-V2X.
We have been proposing and supplying RF connectors required for the systems (Beyond 5G system, Wireless IoT system, and Next Generation Mobility System) that will be realized in 2030. In the Beyond 5G system, we have received strict requests from customers to further reduce electromagnetic noise emitted from connectors (harnesses). At the same time, we are developing connectors that can handle frequencies higher than 45 GHz. In order to satisfy these market requirements, we are developing connectors with higher shielding performance by making full use of connector shapes, optimal wiring methods including ultrasonic wiring, and manufacturing methods.
Related article page: Next Gen. Mobility System connectors
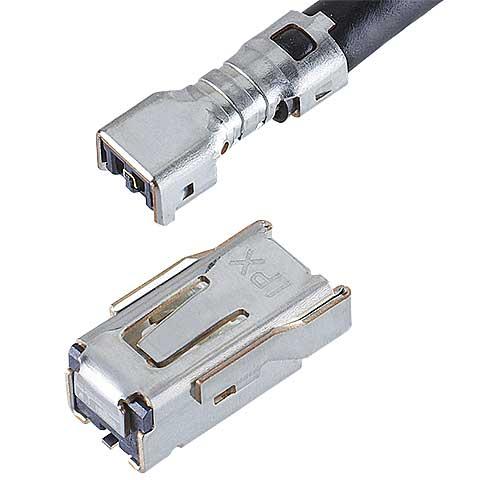

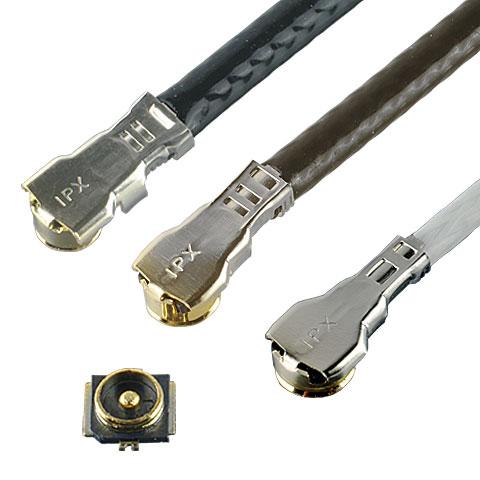
Small, robust SMT connector for automotive telematics antenna |
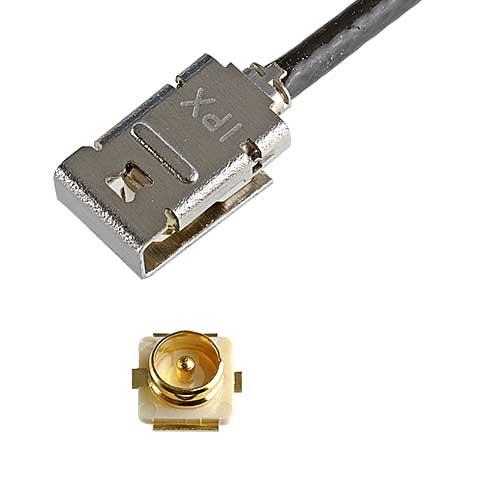

Locking solution that works with MHF I receptacles, supports up to 9 GHz, mated height of 2.9 mm max |
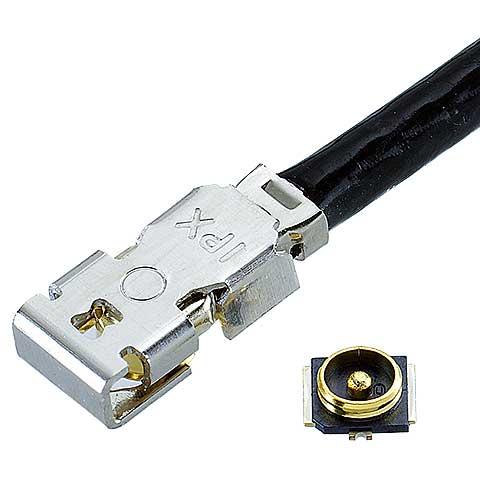

Locking solution that works with MHF 4/4L receptacles, the M.2 industry standard, mated height of 2.0 mm max., excellent electrical performance up to 12 GHz |