极细同轴线/Twinaxial连接器
I-PEX 是极细同轴线连接器的先驱,I-PEX 于 1996 年批量生产了首款 CABLINE®极细同轴线连接器。随着数据传输速率和产品使用频率的提高,I-PEX 极细同轴线/双芯线连接器也在不断发展,以更好的满足市场需求。本页会对极细同轴线/双芯线连接器、电缆和电缆组件的常见问题进行解答,旨在帮助新晋工程师了解首次使用这些产品时的考量要点,以及资深工程师在今后的设计工作中如何更好的使用这些产品。
目录
- 1) 同轴电缆组件
- 2) 双芯电缆组件
- 3) 最大工作频率
- 4) 连接器可用空间
- 5) EMI 屏蔽和电力信号
- 6) 最小化损耗
- 7) 弯曲、弯折和扭转要求
- 8) 引脚分配
- 9) 护套和捆绑类型
- 10) 高速协议
- 11) 线束制造工艺
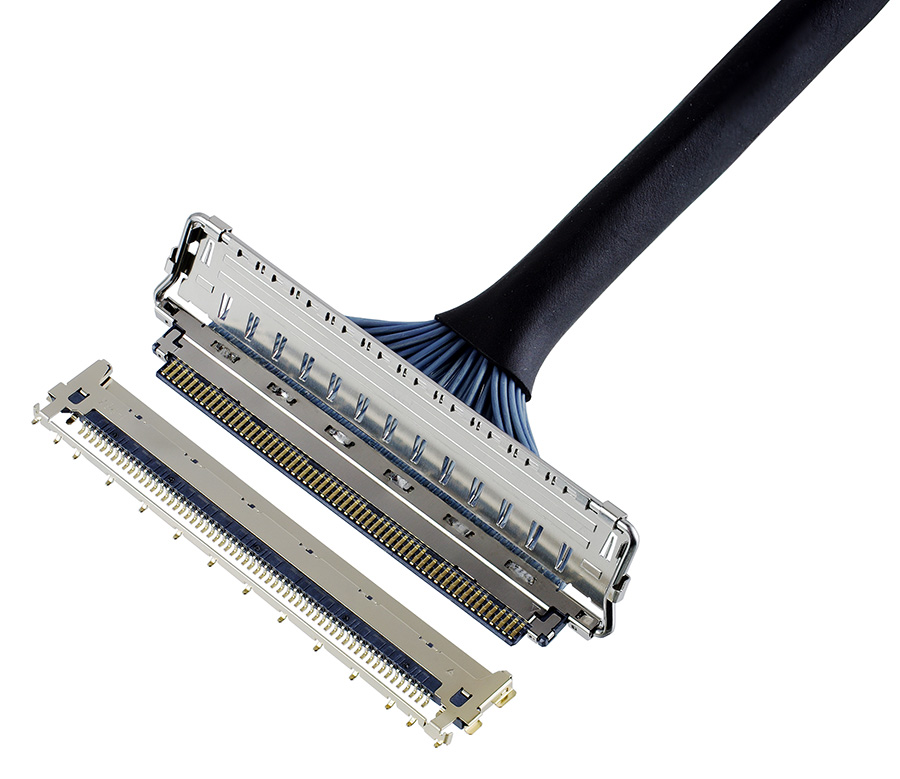
1) 同轴电缆组件
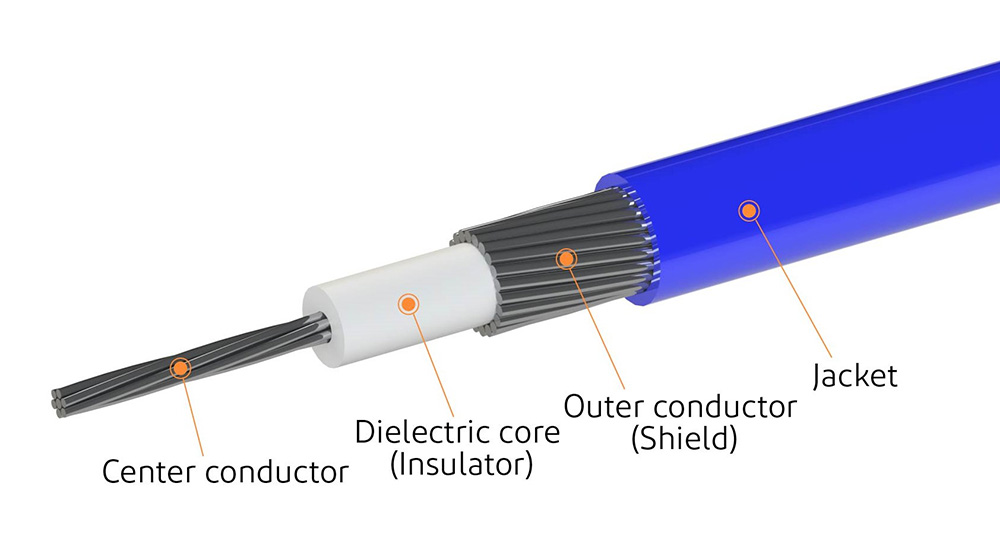
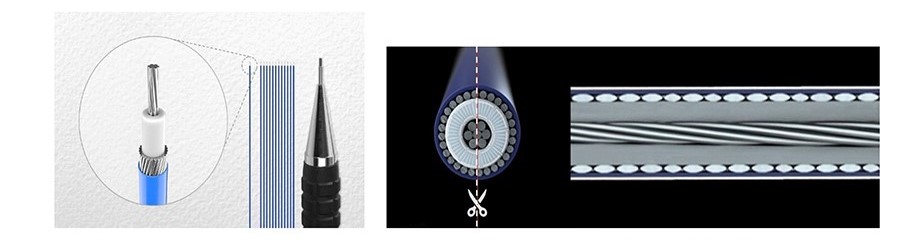
高频信号对来自附近通信源(如天线、高速电路板走线和 PCB 上的收发器)的电磁辐射更为敏感。通过使用极细同轴电缆,这些高速信号可以很好地屏蔽噪音,并保持数据的信号完整性。极细同轴电缆包括一个用于信号传输的中心导体,其周围是用于绝缘的介质,外层导体由多股金属护套组成,用于接地回流,外被护套包裹,用于额外绝缘。I-PEX 可为高频信号提供完整的极细同轴线束解决方案,其全屏蔽款连接器提供机械锁扣的功能,可实现可靠稳固的连接。
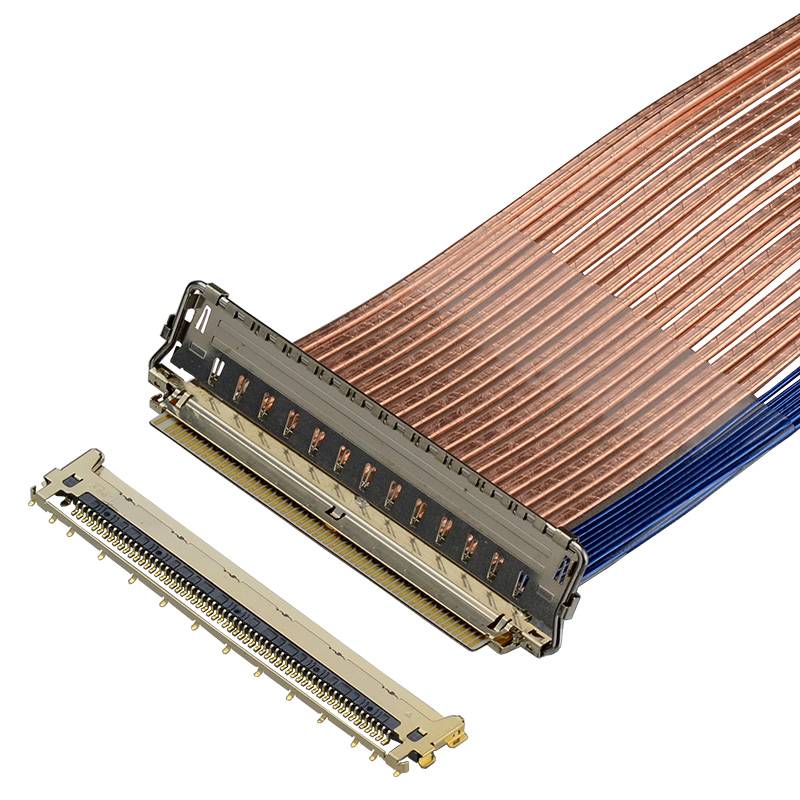
2) 双芯电缆组件
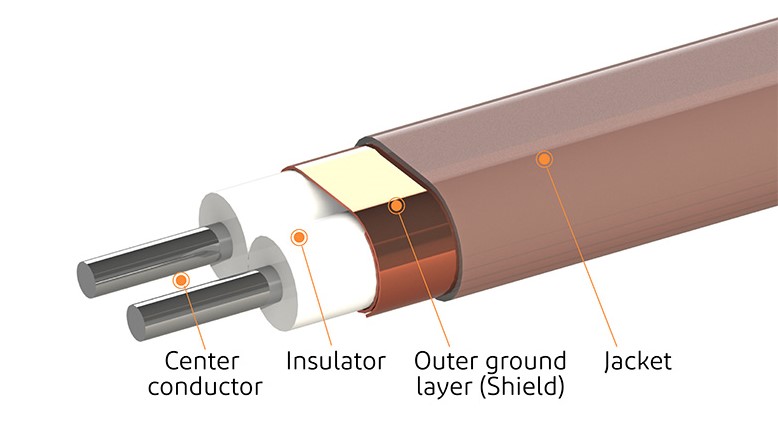
双芯线电缆更适用于低电压、低延时和紧密相位匹配信号的高速数字数据传输。与 PCB 线路相比,这些电缆散热更少,信号损耗更小,因此可用于电路板上设备的互连。双芯电缆有两个中心导体,通常用于差分信号。这两根导体被橡胶或塑料等绝缘体隔开和包围。这些导体周围有一层绝缘介质层,就像极细同轴电缆一样。外层为金属导电屏蔽,用于接地回流,最外层为 PVC 护套。I-PEX 为高速差分信号提供完整的 双芯电缆解决方案,您可使用我们的全屏蔽连接器(可选是否带有机械锁定功能),以实现可靠的连接。
3) 最大工作频率
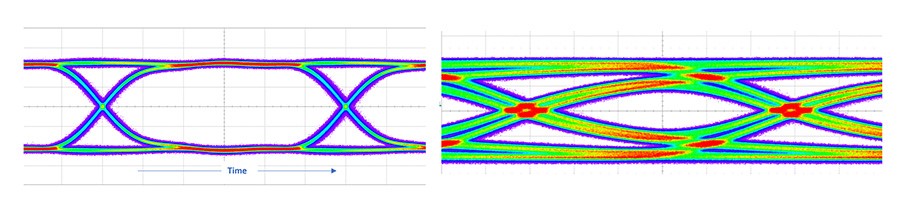
最大工作频率决定了通信系统高速接口的传输速度和数据量。在高速数字数据传输中,互连介质的阻抗失配和高插入损耗会导致信号眼闭合,从而导致高误码率和接收端的数据丢失。因此,使用阻抗匹配良好的高性能、低损耗电缆互连变得更加重要,这样才能高保真地传输高速信号。CABLINE® 系列产品损耗低,工作频率最高可达 16GHz,使用 PAM4 信号可支持高达 64Gbps 的数据传输速率。CABLINE®系列产品通常支持的协议有 USB、eDP、Display Port 和 PCIe。
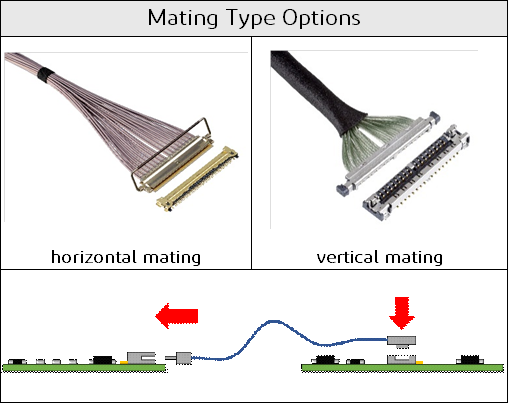
4) 连接器可用空间
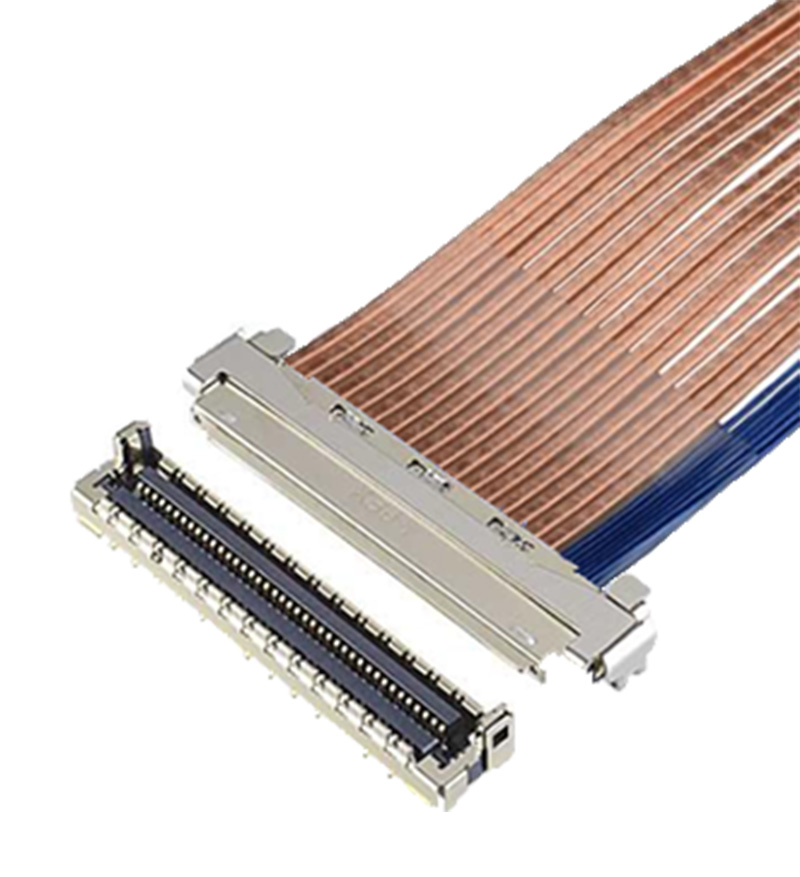
接口的通道数、所需pin数、每个pin之间的间距、公座和连接器的允许配接宽度、长度和外形高度决定了应使用了合适的连接器。连接器在印刷电路板上的最大可用面积和位置也决定了母座和公座线束组件的安装配置,可以是水平的,也可以是垂直的。I-PEX 在其 CABLINE® 系列高速连接器中提供水平和垂直插拔款以及各种不同尺寸和pin数的连接器。
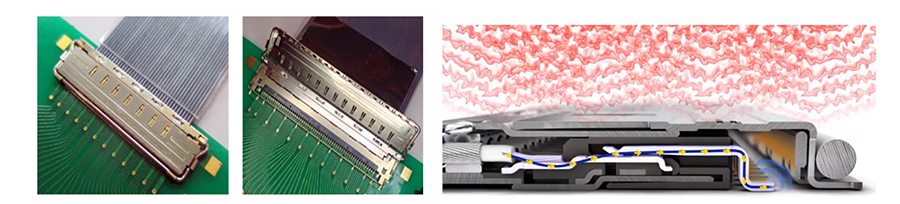
5) EMI 屏蔽和电力信号
有时需要在同一线束中传输电源、低速控制和高速数据信号。由于系统中的表面贴装元件或噪音非常接近,因此需要对信号进行屏蔽,以防止电磁干扰和串扰。I-PEX 全 360 度 EMI 屏蔽解决方案-名为 ZenShield®, 在CABLINE® 系列产品公座的柔性印制电路极细同轴电缆和双芯电缆中,以防止 EMI 噪声干扰已经嵌合的连接器信号端子和焊接尾端。
ZenShield® 适用于 CABLINE®-VS II、CABLINE®-VS IIF、CABLINE®-CA II、CABLINE®-CA II PLUS、CABLINE®-CA IIP PLUS、CABLINE®-CA IIF、CABLINE®-CX II 和 CABLINE®-UM 系列产品。
6) 最小化损耗
插入损耗、回波损耗和驻波比是高速双芯线和极细同轴电缆组件的关键性能指标。在高速应用中,高性能极细同轴电缆可实现出色的信号完整性并降低损耗。 I-PEX提供高性能的 CABLINE® 极细同轴电缆和双芯线电缆组件,这些组件采用自动化装配流程制造,以确保每个成品都具有一致的高质量和低损耗。
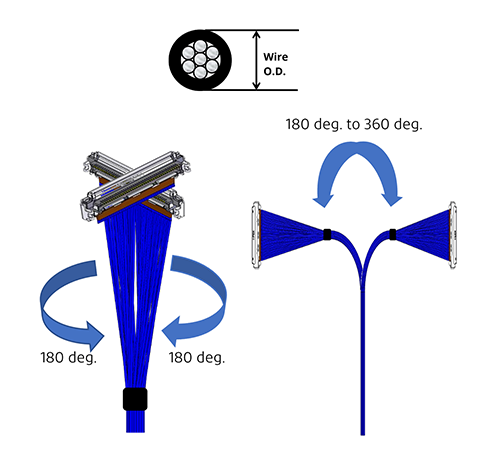
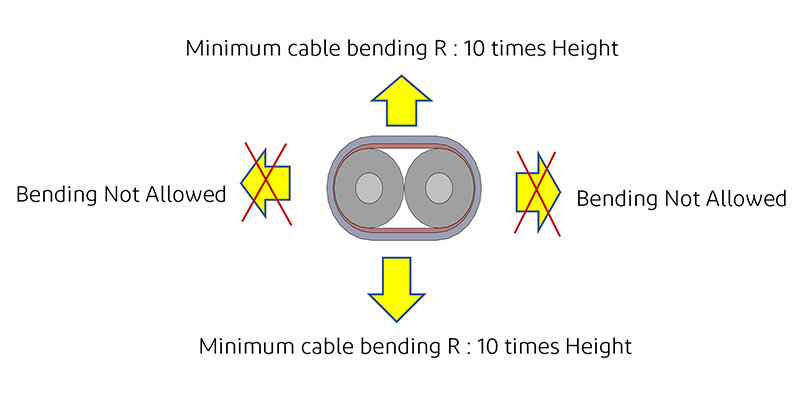
7) 弯曲、弯折和扭转要求
极细同轴电缆和双芯轴电缆都规定了最小弯曲半径,这一参数决定了这些电缆可以在多大程度上反复弯曲而不会损坏,同时还能确保信号的高度完整性。最小弯曲半径通常以毫米为单位。极细同轴电缆还指定了扭转参数,该参数允许电缆沿 Y 轴旋转运动,通常以度为单位。 对于极细同轴电缆,推荐的最小弯曲半径为 "导线外径的6 倍",但实际规格取决于客户选择的同轴电缆。
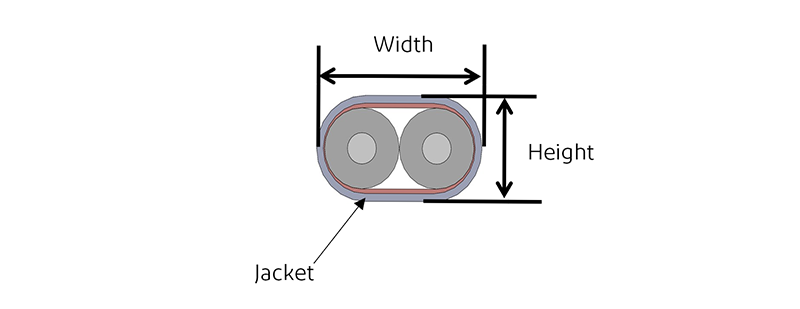
对于双芯电缆,如下图所示,电缆的结构只限制其高度方向的弯曲和挠曲。根据经验,双芯电缆的最小弯曲半径规定为电缆高度的 10 倍。不允许沿 Y 轴方向弯曲和挠曲。
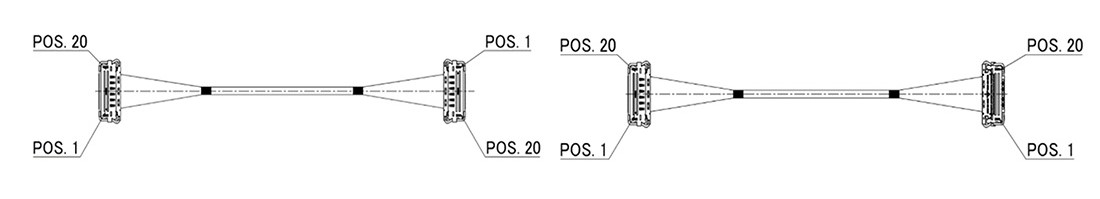
8) 引脚分配
根据信号引脚、布局和电路板走线,线束组件中每个连接器的引脚分配可能不同。I-PEX 高速线束组件提供两种不同类型的引脚分配配置,即 1-N 型直引脚分配和 1-1 型镜像引脚分配配置,可在设计中灵活布线和放置。
9) 护套和捆绑类型
我们为高速电缆束提供四种不同类型的外部胶带或着护套,以提高布线和安装时的设计的灵活性。 捆扎胶带可多点缠绕电缆,覆盖线束的部分、大部分或全部布线区域。此外,还有扁平捆绑类型可供选择,适用于空间有限的系统,这些系统需要重量轻、透明、散热快和应力分布均匀的外护套。
10) 高速协议
USB 3、USB 4、Thunderbolt、Displayport、eDP、HDMI、MIPI 和 PCIe Gen 5 和 Gen 6 是一些通常支持的协议,使用 PAM4 信号类型,最大数据传输速率为 64Gbps/Lane。
I-PEX 提供的工具可用于查找适用于特定行业标准(如 MIPI、PCIe、USB 等)的可用连接器选项。同时,用户还可以通过该工具了解 I-PEX 高速连接器系列支持哪些类型的行业标准。
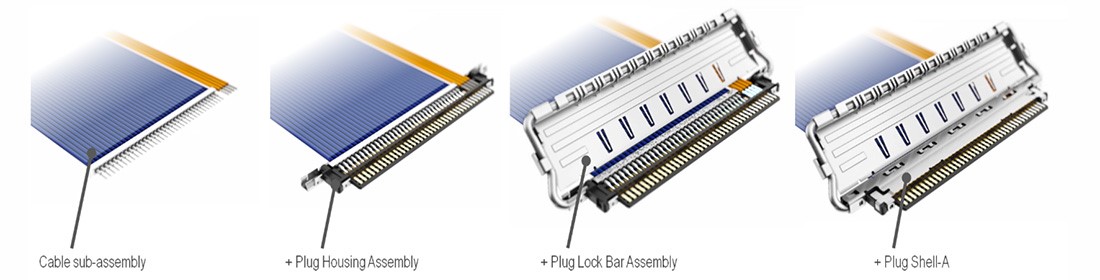
11) 线束制造工艺
公座线束准备的主要流程如下:
- 剥线并准备电缆组件
- 将电缆子组件安装到公座外壳组件部分,并将裸露导体焊接到公座信号端子上
- 将锁定杆组件(或锁定杆)安装到公座外壳组件上
- 盖上公座外壳并焊接所需区域,完成公座线束制程