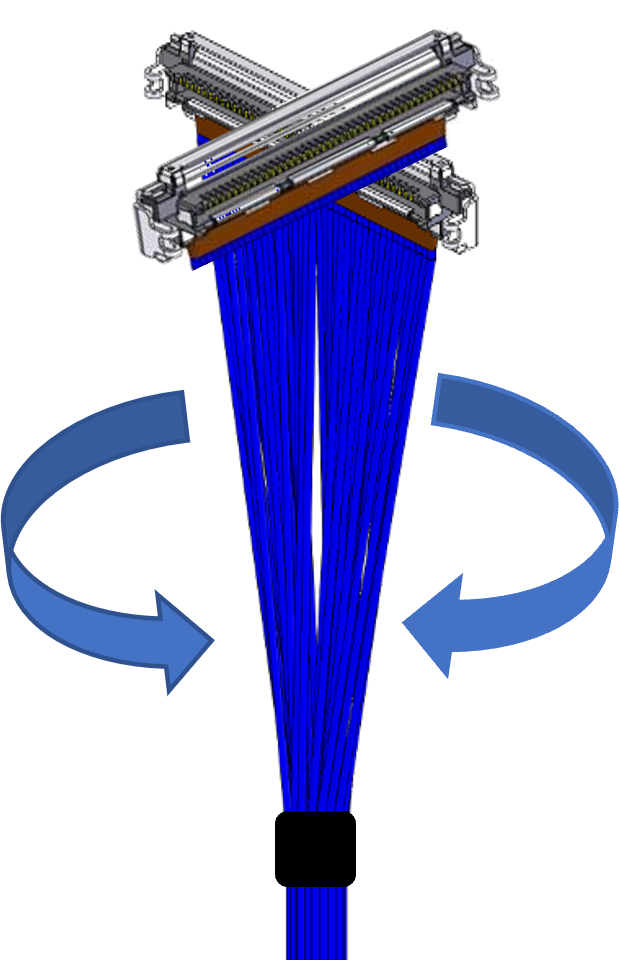
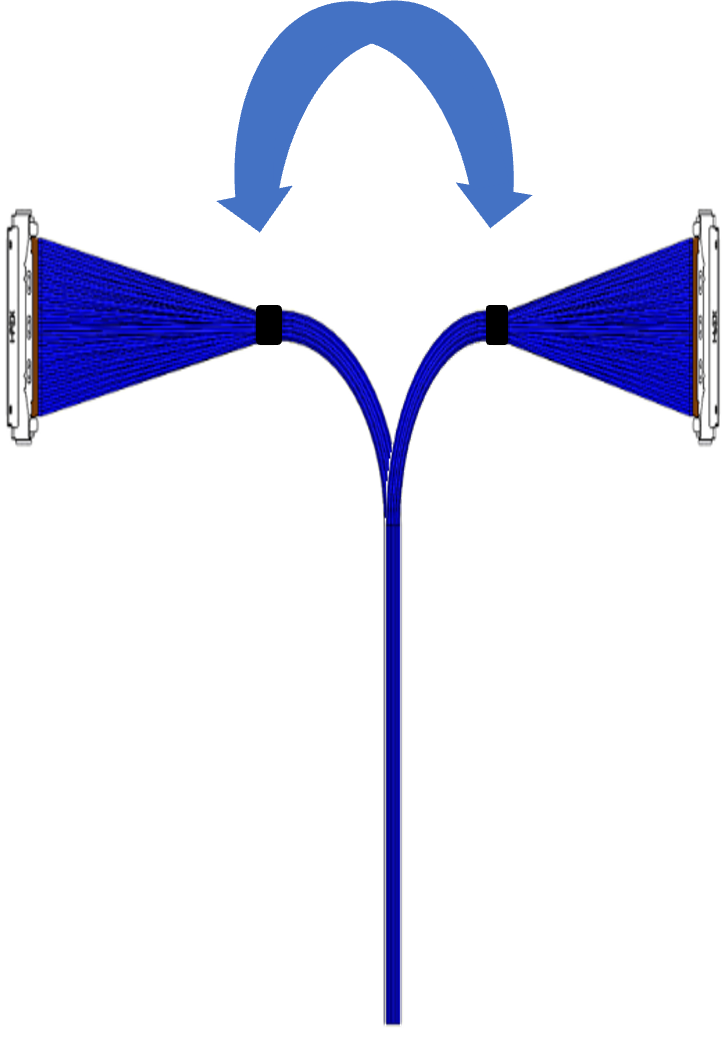
Bend Flex and Twist Requirements
It is important to consider the bending and flexing properties of high frequency Micro-coaxial and Twinaxial cable assemblies, when designed into new smaller, compact portable electronics. Both Micro-coaxial and Twinaxial cables are specified for Minimum Bend Radius, a parameter that determines how tightly these cables can be bent repeatedly with out being damaged and still ensuring high signal integrity. Minimum bend radius is typically measured in millimeters. A typical use case of Micro-coaxial cables is to provide the connectivity between the display and motherboard in systems using hinge. Micro-coaxial cables are also specified for twisting, a parameter that allows the rotational movement of cable along the Y axis and is typically measured in degrees.
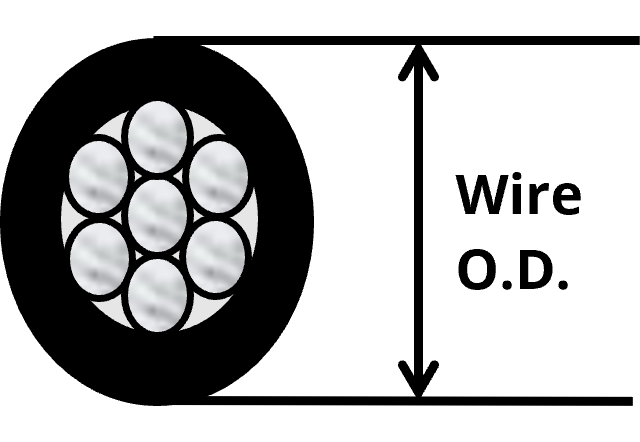
When it comes to Micro-coaxial Cables, the recommended minimum bending radius of cable is “6 times Wire O.D" but the actual specification depends on customer's selected coaxial cable.
|
|
|
Microcoax cables are tested for bending and flexing performance by using a test fixture which allows to bend the cables at +/-90 degrees under load conditions. Idea is to stress the cables with multiple bending/ flexing cycles and measure the S-parameters of cable after a certain number of cycles. The S-parametric performance after the completion of bending/ flexing cycles is compared with the S-parametric performance of initial samples before the tests. The cables are also inspected at the end of test cycles for any mechanical failures including wire breaks. Bending/ Flexing performance of Micro-coaxial cables is listed in the Table 1. below :
Bending radius/group |
Test sample ID (AWG#44)
|
Avg. |
||||
|
|
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
|
1mm / No.1 |
3.5K |
4.2K |
4.2K |
3.4K |
4.3K |
3.9K |
2mm / No.2 |
25K |
30K |
26K |
30K |
28K |
28K |
5mm / No.3 |
400K |
600K |
500K |
600K |
450K |
500K |
Table 1. Bend/ Flex Performance of Coax Cable
Similarly, Micro-coaxial cables are tested for twisting performance by using a test fixture which allows to rotate/ twist the cables along Z-axis by +/-180 degrees under load conditions. Idea is to stress the cables with multiple twist cycles and measure the S-parameters of cable after a certain number of cycles. The S-parametric performance after the completion of Twisting cycles is compared with the S-parametric performance of initial samples before the tests. The cables are also inspected at the end of test cycles for any mechanical failures including wire breaks. Twist cycle performance of Micro-coaxial cables is listed in the Table 2. below :
Test condition |
Test sample ID (AWG#44) (times) |
Average |
||||
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
||
+/- 180 deg. |
>900K |
>900K |
>900K |
>900K |
>900K |
>900K |
Table 2. Twisting Performance of Coax Cable
When it comes to Twinaxial Cables, the construction of cable restricts the bending and flexing in the direction of its height only as shown below. Since the two conductors are placed side by side separated by solid dielectric in the cable, bending side ways can damage the cable physically also impacting the electrical performance and the signal integrity of data.
As a rule of thumb, the Minimum Bend radius for Twinaxial cables is specified as 10 times the height of cable as shown below.
|
Minimum cable bending R : |
||
|
Bending Not Allowed |
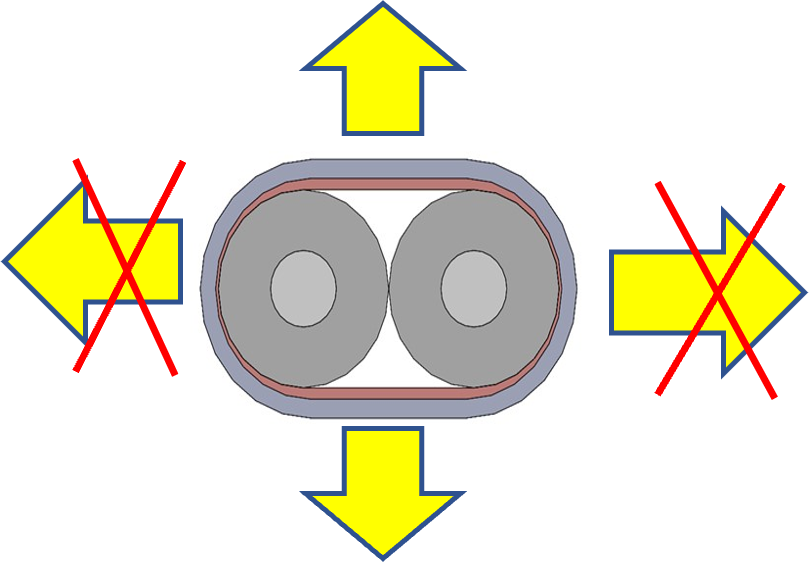
Minimum cable bending R : |
Bending Not Allowed |
|
Width 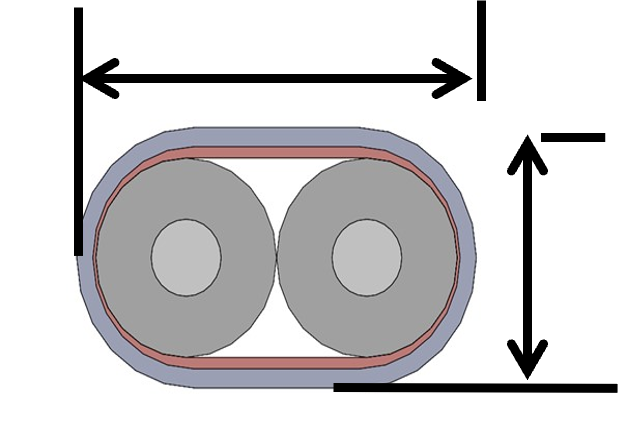
↑ Jacket |
Height |