Main Process of Plug Harness Preparation
Main Process of Plug Harness Preparation is as follows:
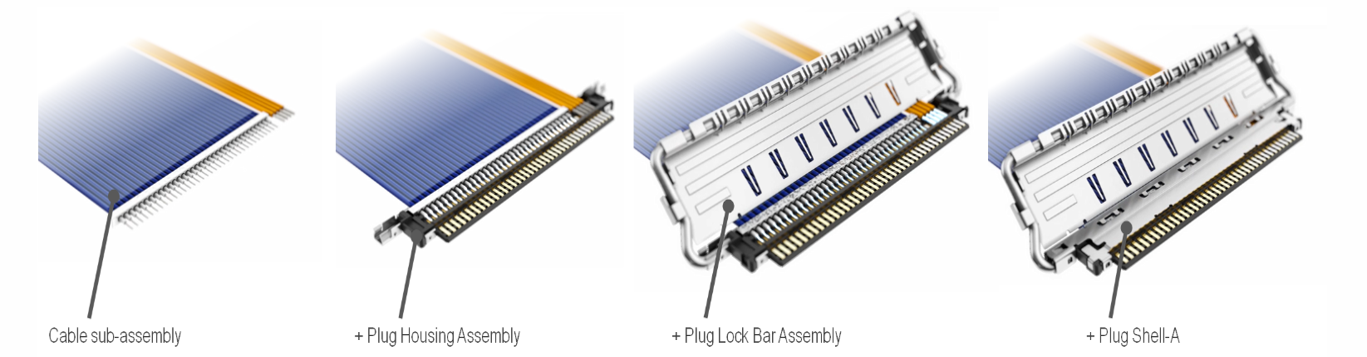
1. Strip and prepare cable sub-assembly
2. Set the Cable Sub-Assembly to the Plug Housing Assembly part and solder the exposed conductor to the plug signal terminal
3. Set Lock Bar Assembly (or Lock Cover) to Plug Housing Assembly parts. Lock bar feature is available in CABLINE®- VS, VS II, CX II, CA, CAP, CAL, CA II, CA IIP, CA II PLUS, CA IIP PLUS, UM, VSF, VS IIF, CAF, CA IIF, CA IIF PLUS series products.
4. Cover the plug shell and solder the required area to complete the plug harness
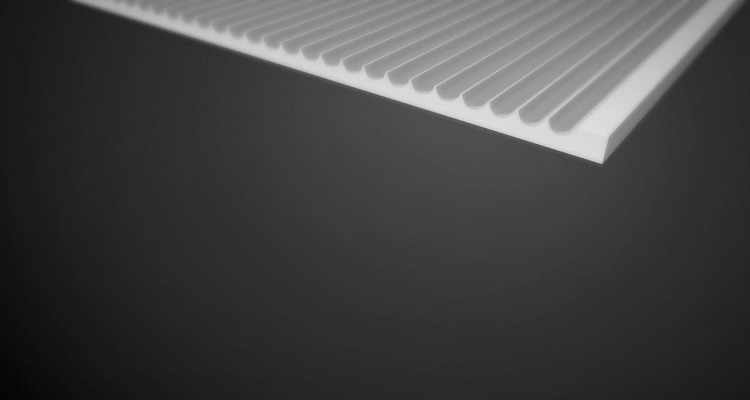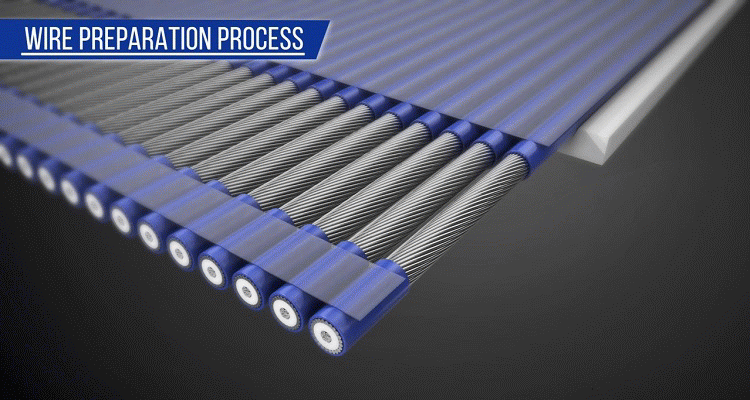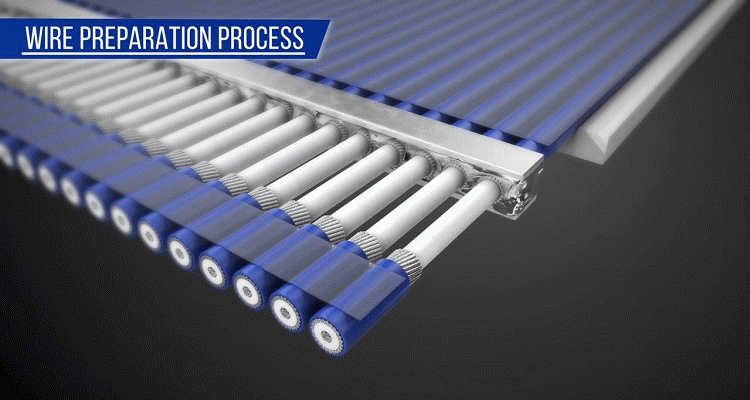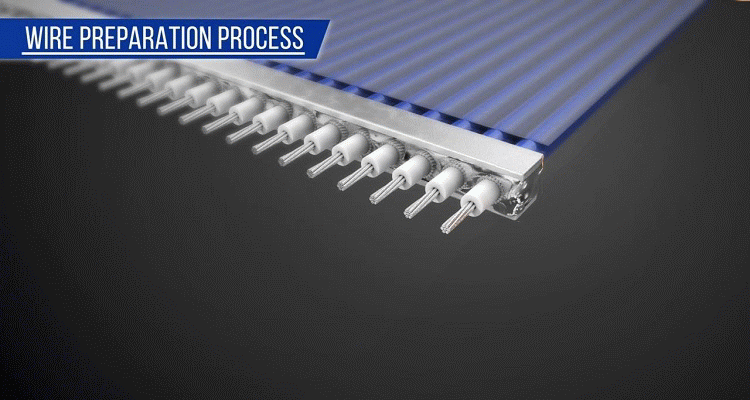
First, pre-process the micro-coaxial cables for easy plug harness assembly. A pre-processed cable is called a "cable sub-assembly". This pre-processing simplifies the cable termination process to the connector and improves the plug harness quality. This is done before terminating the cables to the connector
 |
|
Types of Cable Sub-Assembly Supported
Generally, the following cable types are available for cable sub-assemblies (dependent on harness makers):
All micro-coaxial cable:
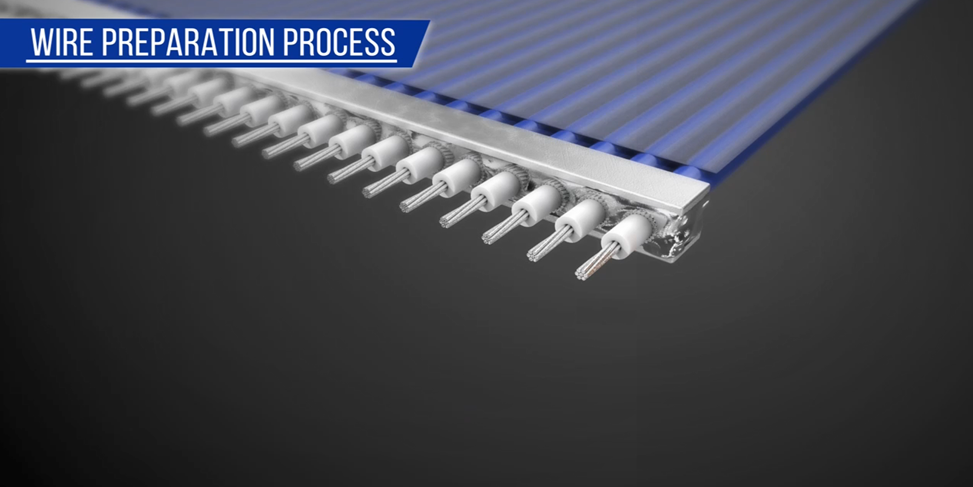
Only micro-coaxial cables are used. Cable sub-assemblies can be made with different cable diameters (diameter size range may be limited).
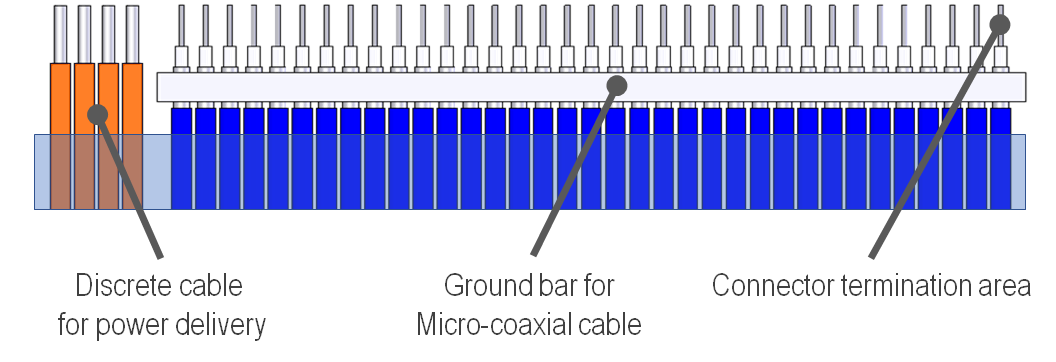
Micro-coaxial/discrete cable mixed:
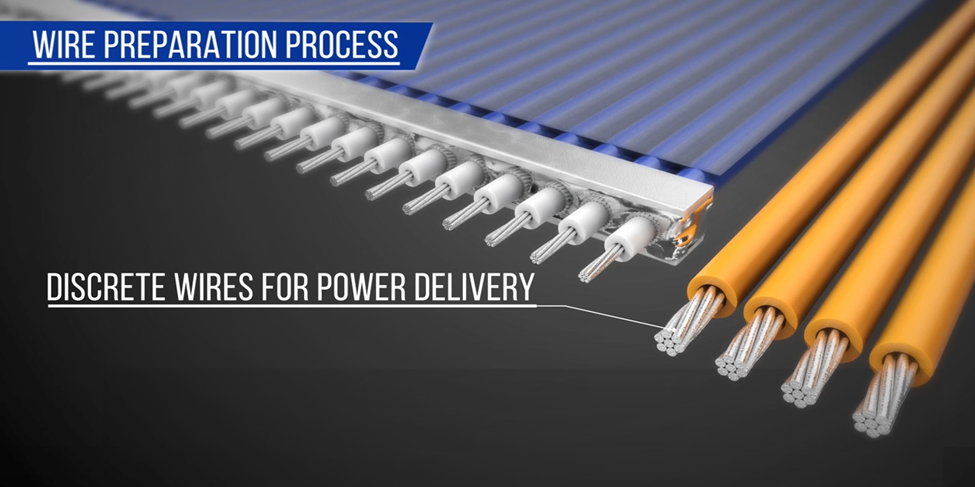
Both micro-coaxial cables for high speed signal transfer and discrete cables for power supply are used.
Ground bar with ground fingers:
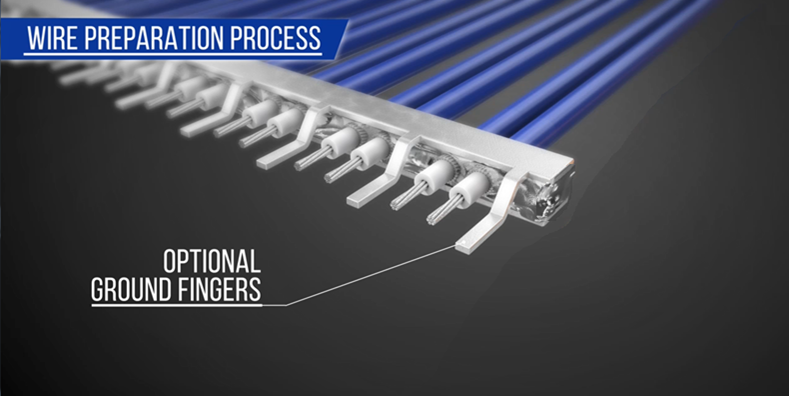
The fingers formed on the ground bar are directly attached and soldered to the plug contacts. This reduces the number of cables used and improves the electrical characteristics performance of the harness.
What is a Micro-Coaxial/Twinaxial Connector?
- 1) Micro-Coaxial Cable Harness
- 2) Twinaxial Cable Harness
- 3) Maximum Operating Frequency
- 4) Available Real Estate For Connector
- 5) EMI Shielding and Power Signals
- 6) Minimizing the Losses
- 7) Bending, Flexing and Twisting Requirements
- 8) Pin Out Assignments
- 9) Jacketing and Bundling Types
- 10) High-Speed Protocols
- 11) Harness Manufacturing Process
