Profile Heights
Using board-to-board connectors with varying profile heights provides designers with the flexibility to optimize performance, reliability, and space efficiency in complex multi-board systems. Design flexibility, improved air flow and thermal management, reduced mating/ demating interference, efficient use of space for lower EMI, enhanced mechanical stability, scalability of systems and support for multi-function systems are some of the key advantages of using these connectors with varying profile heights.
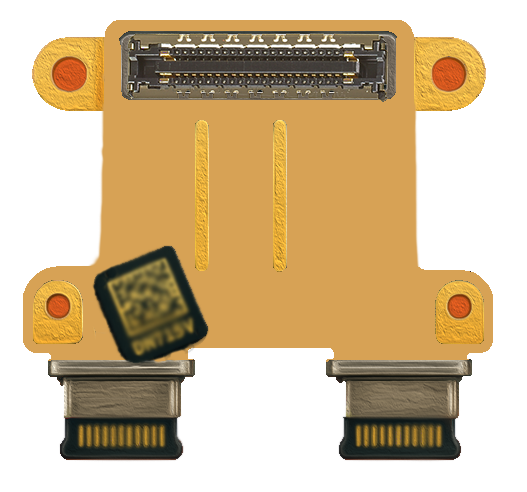
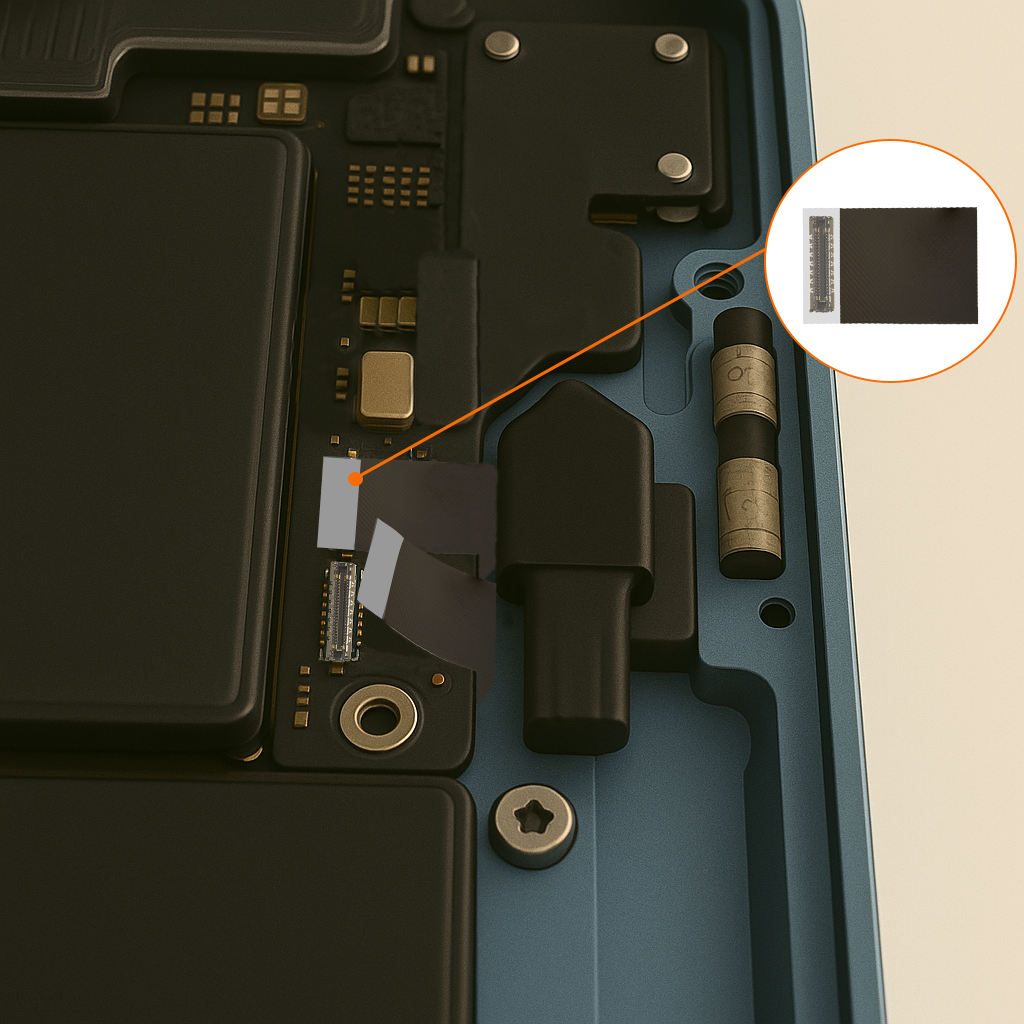
Different profile heights allow designers to customize the spacing between boards, enabling optimal placement of components and efficient use of vertical space with out the use of additional spacer components. Systems designed with varying profile heights are more adaptable, allowing additional boards to be added in the future without a complete redesign. Also, these connectors enable integration of boards with distinct functions (e.g., power management, signal processing, and I/O interfaces) in a compact, modular architecture. Modular architecture of sub systems like Display Screens, Battery banks, USB ports and camera modules using the Flexible Printed Circuits and board to board connectors makes the systems easily repairable without soldering. Some examples of USB type C port connector modules in Notebook computers and camera subsystem modules in AR/VR glasses, using board to board connectors and flexible printed circuits are shown in the Figure 1. below.
 |
 |
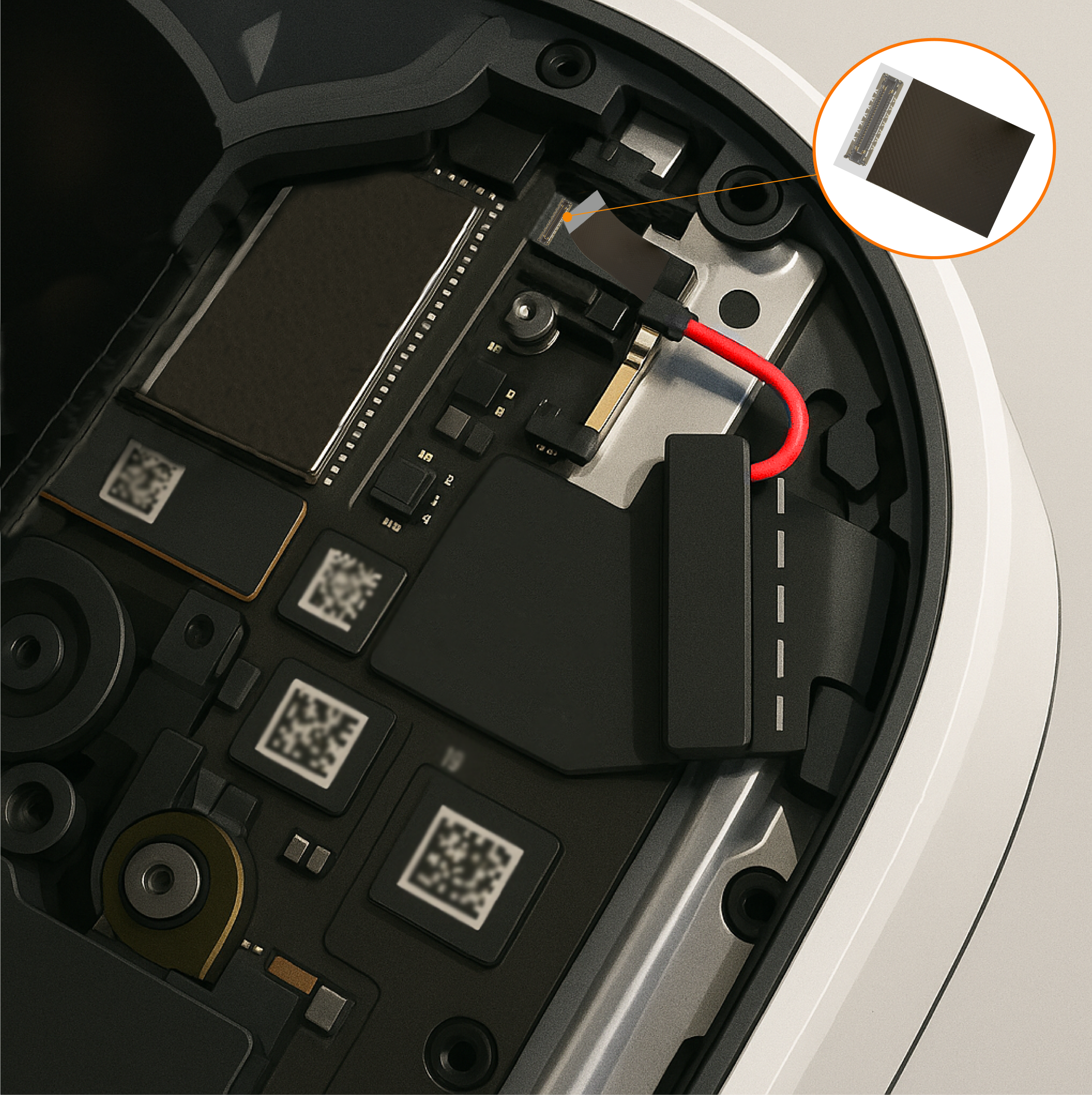 |
Figure 1. USB type C Connector Modules and Camera Subsystems Using Board to Board Connectors and FPCs
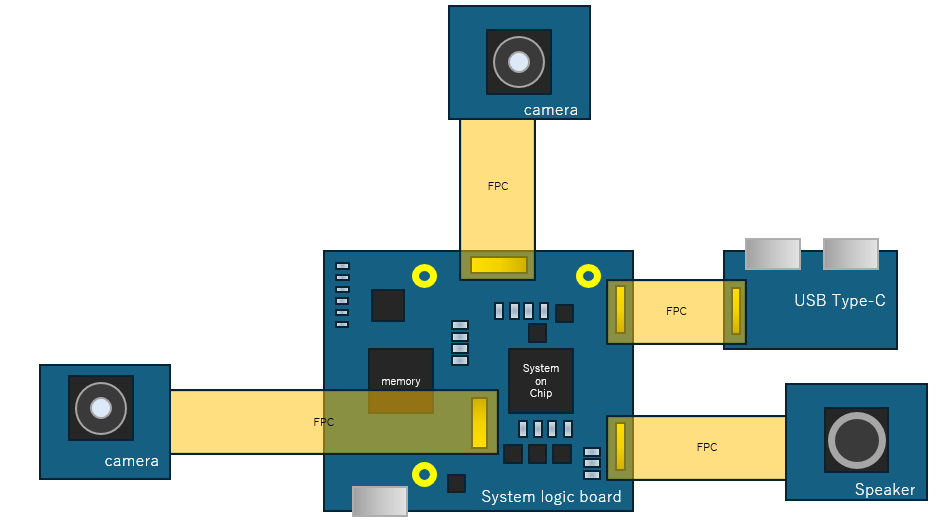
Often times, in a high density, crowded circuit board, there is a need to connect multiple subsystem modules to main logic board and there are surface mounted components in close proximity of connector. A high profile board to board connector like NOVASTACK® 35-HDH can be used with flexible printed circuit to jump over such components saving board space without any interference. Figure 2 shows such a connection of multiple camera subsystems with the System logic board using board to board connectors and FPCs. Such an interconnection of boards eliminates the extra components to adjust the board height, makes the systems modular, compact and repairable extending the overall life cycle and saving the cost.
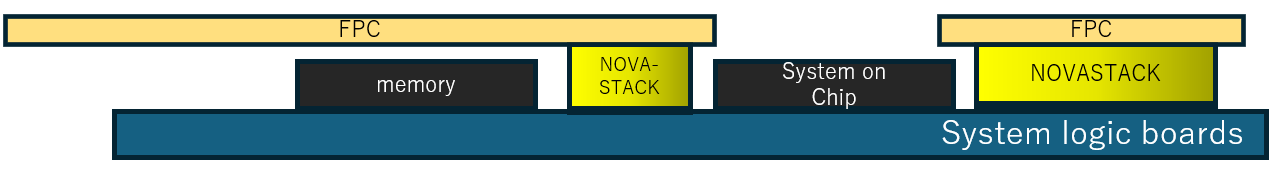
Figure 3 shows another example of using board to board connectors with different stack up heights in compact systems with horizontal and vertical space constraints. Multiple subsystem boards can be connected with the main board offering more flexibility to route the flexible printed circuits with minimal interference.