What is MEMS? (Detailed explanations with diagrams)
This page provides a detailed explanation of MEMS, which use semiconductor processing technology commonly found in everyday products.
Contents:
What is MEMS?
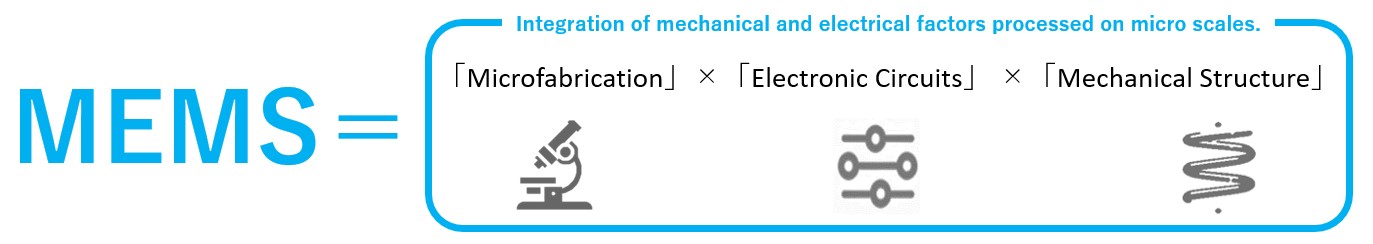
MEMS (Micro-Electro-Mechanical Systems) is systems that integrate mechanical structures and electronic circuits processed on micro scales.
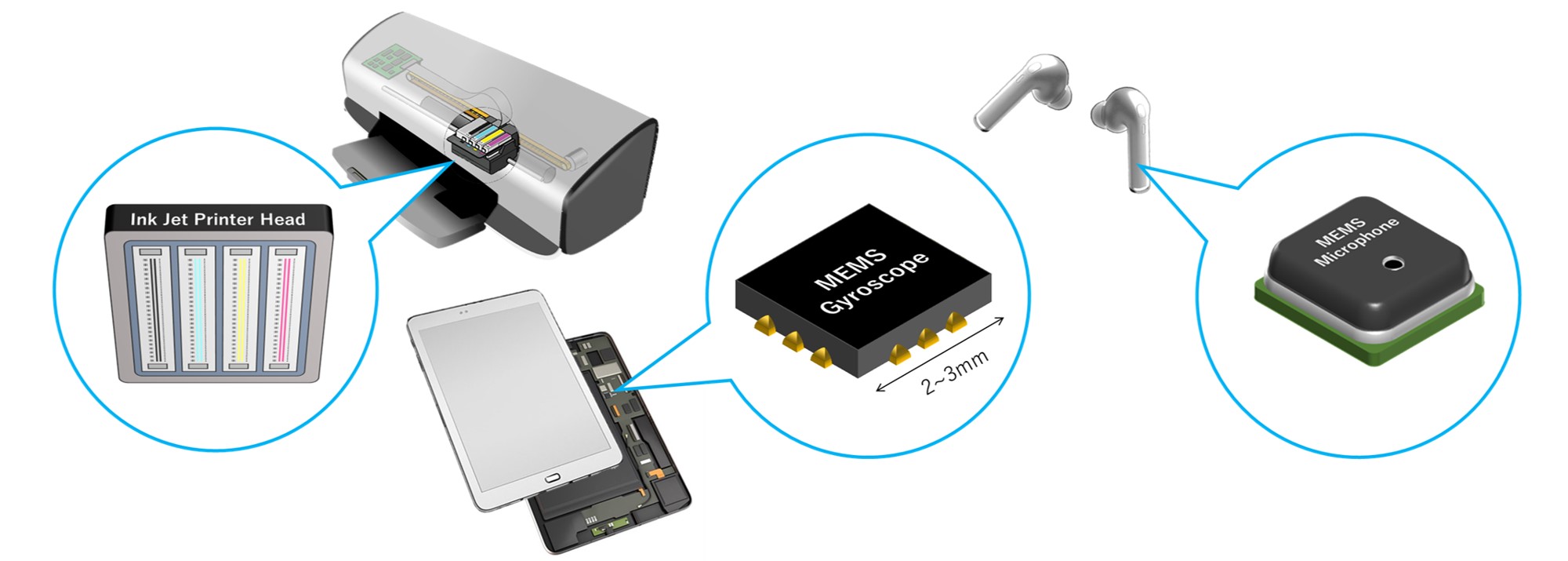
Examples of typical MEMS devices include accelerometers, gyro-sensors, pressure sensors, micromirrors, inkjet printer heads, microphones, and speakers.
These MEMS devices are often manufactured and assembled using semiconductor processing techniques, with micro-mechanical structures and electronic circuits integrated onto chips (MEMS chips) on wafers. MEMS are already used as electronic components in a wide range of fields—including home appliances, automobiles, IoT products, telecommunications, and medical devices—and their use is expected to continue growing in the future.

MEMS and Semiconductor Technology
Widely used MEMS devices are manufactured using semiconductor technology in the similar way as IC chips. They are therefore both precisely manufactured on a very small scale. Specifically, advanced semiconductor processing methods such as deposition, photolithography and etching technologies are used.
The main reasons why semiconductor processing technologies are widely used in MEMS are that the semiconductor silicon substrates used in IC chips have excellent mechanical and electrical properties as a material for MEMS. Also, advances in IC technology have led to the development of silicon substrate microfabrication technology, integration technology, standardized mass production processes and the deployment of high-performance process equipment to enable these processes, which have greatly improved the precision, functionality, productivity and cost-efficiency of MEMS devices.

MEMS technology utilizes many of the manufacturing techniques and processes established by the IC technology, enabling increased productivity and cost reductions, resulting in the increased use and widespread adoption of MEMS in a wide range of industries.
*Some MEMS use a variety of processing technologies and materials other than semiconductor technology, such as micro-machining, 3D printing and polymer materials, as well as those that have no moving parts, such as optical waveguides and DNA chips.
Differences between MEMS and ICs
MEMS and IC have many similarities in terms of manufacturing methods and size reduction technology, yet there are significant differences in their functions, applications and operating principles. MEMS are systems related to physical movement and measurement, while IC are circuits that perform purely electronic signal processing. Both play an important role in modern technology and are used in applications that are suited to their specific characteristics.
IC consists of purely electronic circuits, which process and control electrical signals using transistors, capacitors and resistors, etc. IC is mainly used in electronic devices for logic calculations, signal processing, memory, etc.
MEMS, on the other hand, are systems that perform mechanical operations and physical measurements and consist of sensors and actuators (drive units). MEMS differ greatly in their applications, appearance, internal structure and size, depending on their use. Typical examples include acceleration sensors, pressure sensors, microphones and speakers.
If ICs specializing in information processing and memory functions can be compared to the human brain, then MEMS, which have various physical functions by combining mechanical movements and sensors, can be compared to the body's functions and sensory organs.
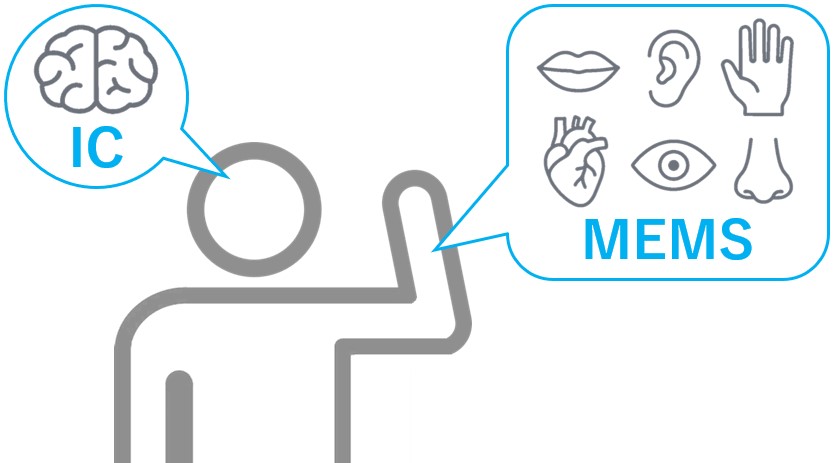
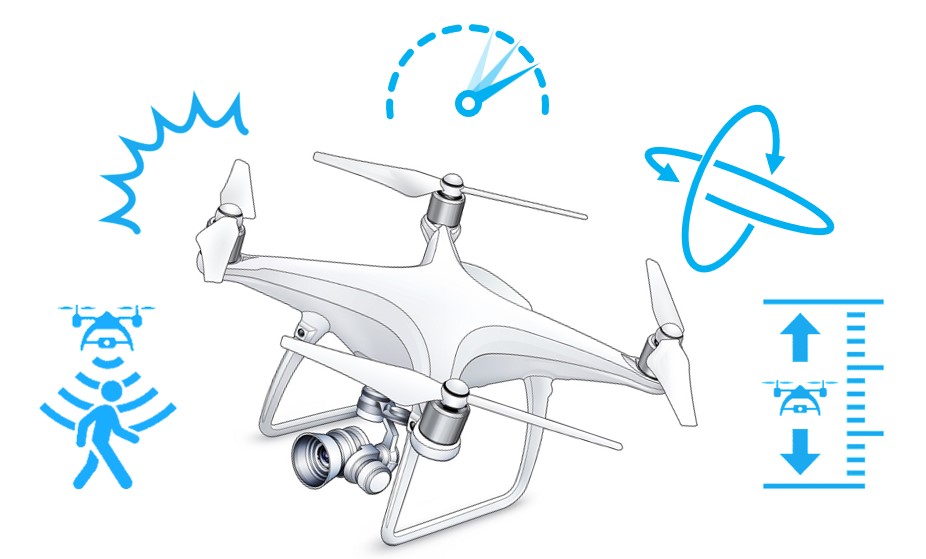
For example, drones are constantly changing their posture due to wind, gravity, and inertia during flight. Also, when flying near people or in confined indoor spaces, the drone must react quickly to its surroundings. If the response is slow, the drone may run into objects or fall. Therefore, in order for the drone to fly stably, it is important to monitor the surrounding conditions in real time and constantly adjust its flight.
MEMS is a very small device that can achieve high performance and low power consumption, making it indispensable for applications that require precise and quick control in response to the surrounding conditions.

How MEMS Work
There are several different types of mechanisms that drive the “small machine” MEMS. Here we will introduce three major types.
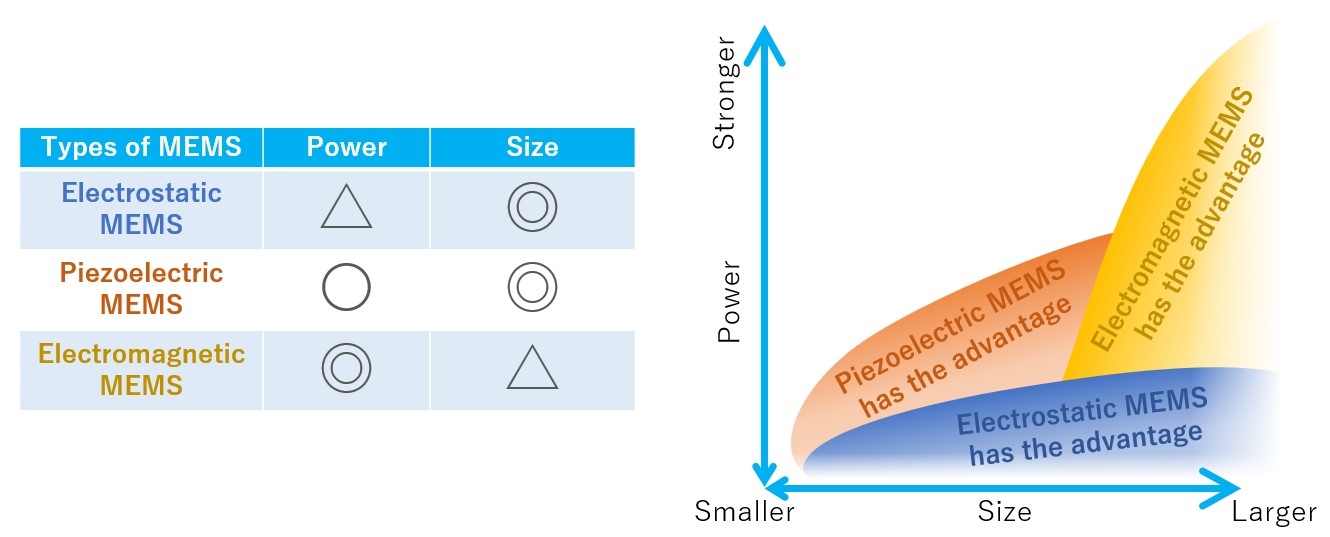
Mechanism of Electrostatic MEMS
Electrostatic MEMS is the most common type of MEMS and is one of the most popular types used as the driving principle of MEMS.
As the name “electrostatic” indicates, Electrostatic MEMS moves using “electrostatic force.” Electrostatic force refers to the force of attraction between + and - electric currents, and for example, small pieces of paper attach to a balloon when it is rubbed with wool. This is also caused by the force of the electrostatic.
When utilizing the power of electrostatic charge in MEMS, small electrodes facing each other are used. When a positive (+) voltage is applied to one electrode and a negative (-) voltage to the other, the two electrodes are attracted to each other and try to come closer together. The larger the area and number of electrodes facing each other, the greater the output and accuracy, so most of the Electrostatic MEMS have multiple electrode pair structures.
For example, an electrostatic MEMS accelerometers has a structure in which a “weight” is supported by springs, and when acceleration is applied, the weight moves due to inertial force. Acceleration can be measured by detecting this movement as a change in the distance between the electrodes.
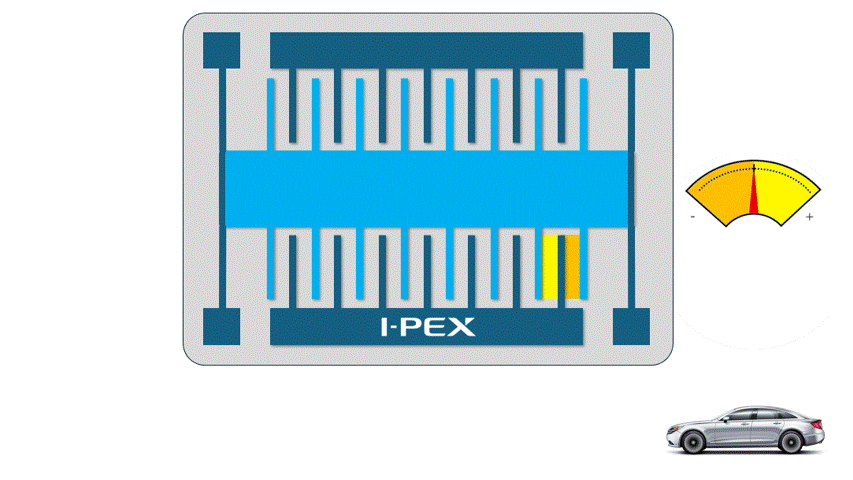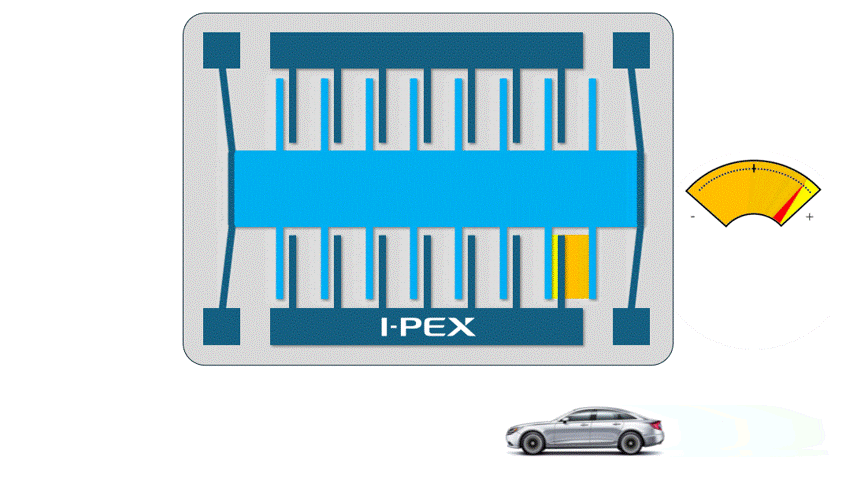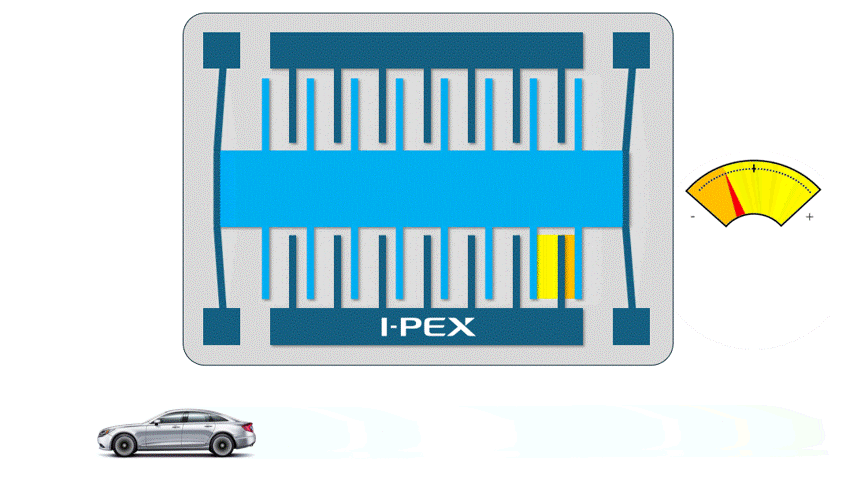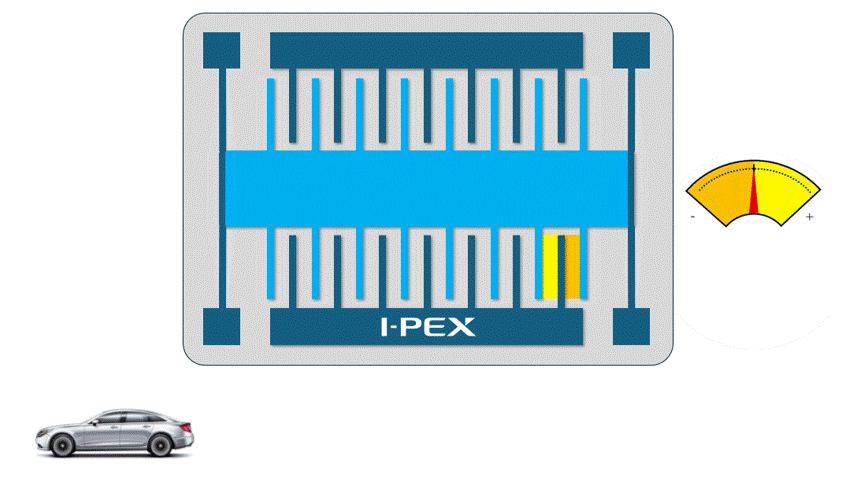
Electrostatic MEMS are compact and consume very little power, making them very suitable for devices that need to run on batteries for long periods of time. However, since electrostatic power is not a very strong, they are not very good at moving objects as “actuators”.
Mechanism of Piezoelectric MEMS
Piezoelectric MEMS is a type of MEMS that works by utilizing a special property called the "piezoelectric effect”.
The piezoelectric effect is a phenomenon in which electricity is generated when a force (pressure or strain) is applied to a certain type of crystal or material, or vice versa, and the material is deformed when a voltage is applied. Piezoelectric materials such as lead zirconate titanate (PZT) and aluminum nitride (AlN) are often used in piezoelectric MEMS.
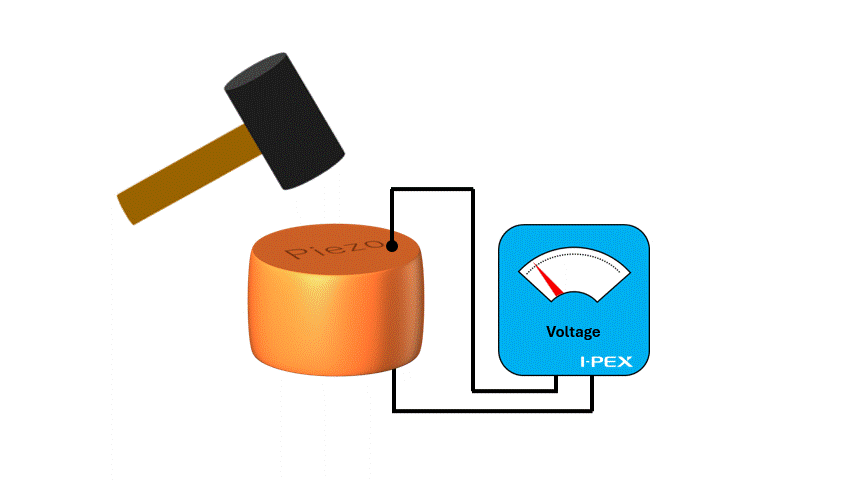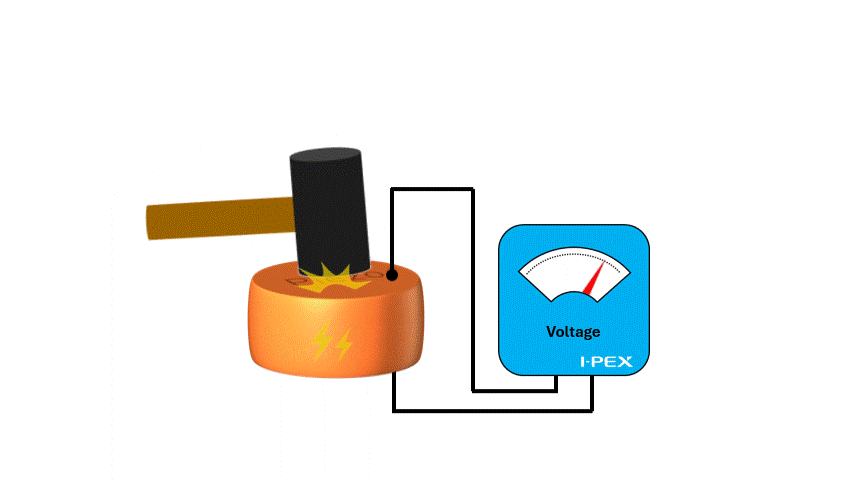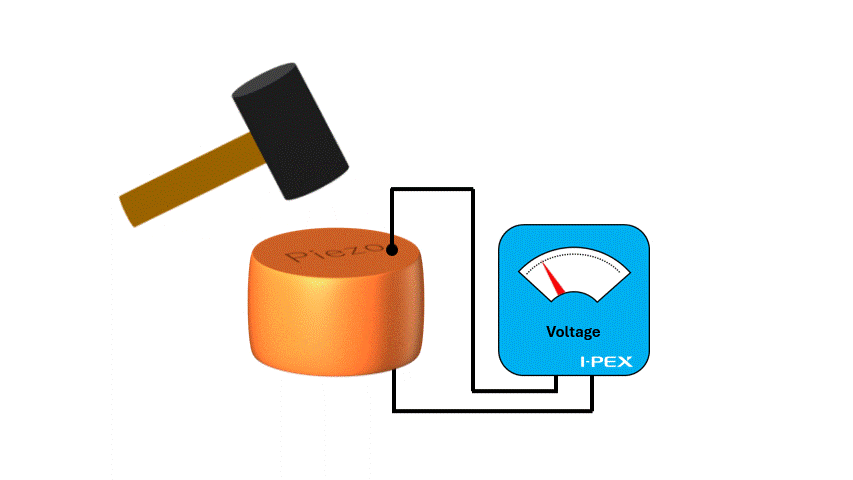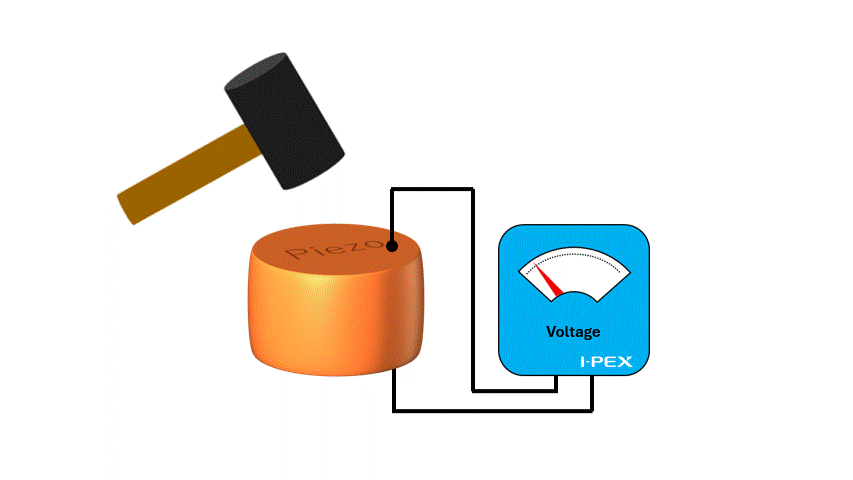
When utilizing the mechanism that electricity is generated when a force is applied to piezoelectric material, it is possible to use it as a "sensor". For example, in a MEMS microphones, air vibrations (sound) hit a membrane and vibrate, and the piezoelectric material converts this force into electricity, which can be used to extract sound as an electrical signal.
Since the material itself senses the “force” and generates electricity without supplying energy from the outside, it is very efficient and high-performance as a sensor. Also, the response is very fast, making it suitable for real-time sensing.
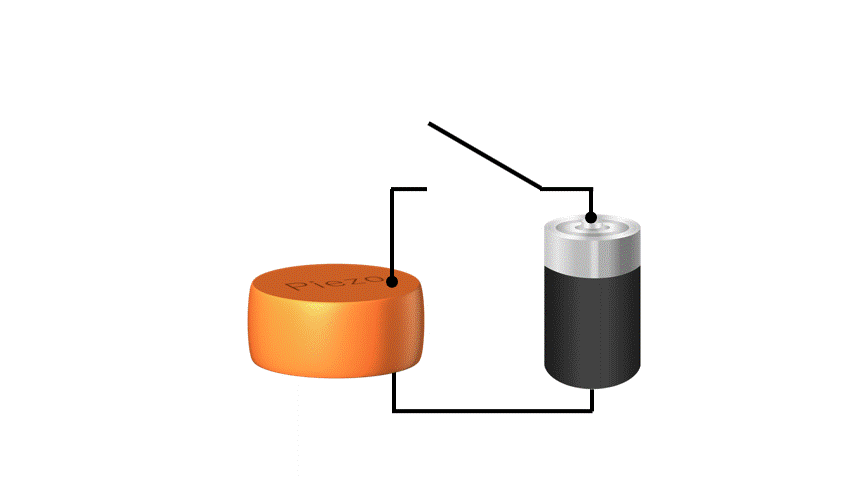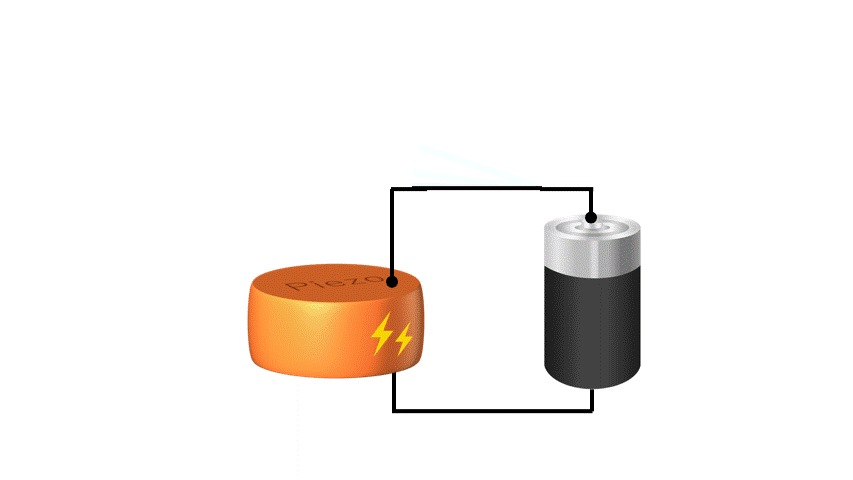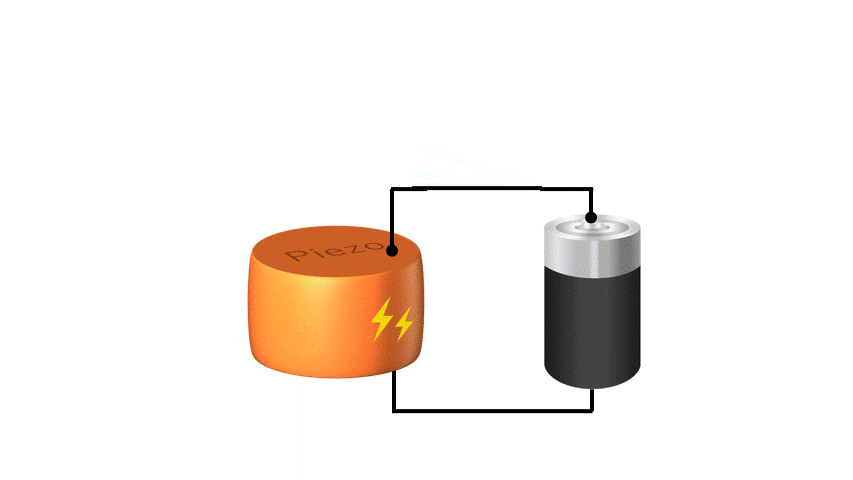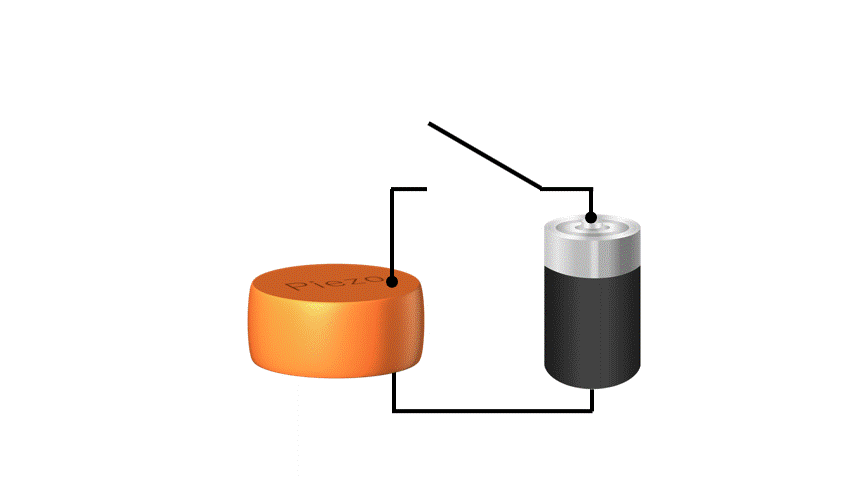
Conversely, when voltage is applied to a piezoelectric material, the material stretches or shrinks slightly, and this movement can be used to move small parts. This feature can be used as an “actuator” such as a MEMS speakers or a MEMS mirrors.
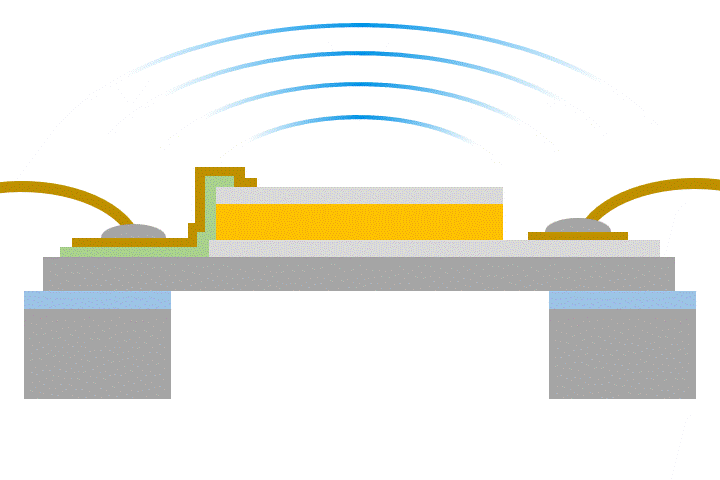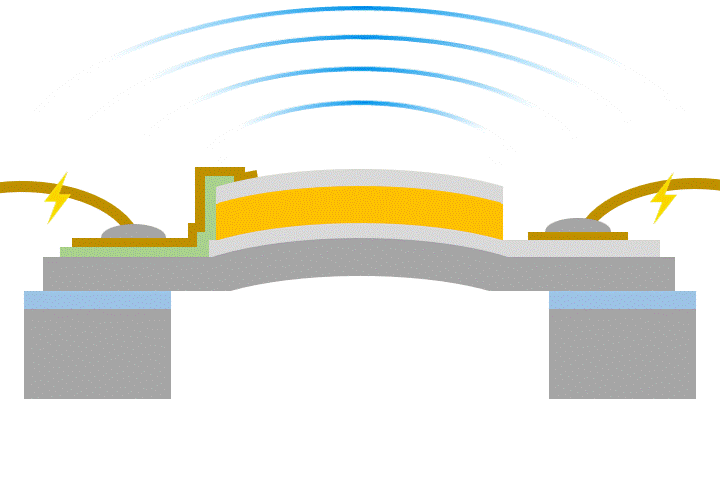
Piezoelectric materials can directly convert “force and electricity” in both ways, so piezoelectric MEMS have a simple structure and are excellent for miniaturization yet can generate stronger forces than electrostatic MEMS. KRYSTAL Wafer's single-crystal PZT film, deposited using superior single-crystal piezoelectric deposition technology, has high voltage resistance and large displacement, making it possible to achieve high performance piezoelectric MEMS.
Mechanism of Electromagnetic MEMS
Electromagnetic MEMS integrate small coils and magnetic materials, and the electromagnetic force generated by passing an electric current through the coils is used to drive the MEMS.
The strength of electromagnetic MEMS is that the power can be increased by the combination of magnetic force and electric current, making it suitable for applications that require higher power output. For example, electromagnetic type micropumps can provide some firm driving force even in small size, so they are used in small medical devices and chemical analyzers that need to move minute amounts of liquids or gases.
However, because electromagnetic MEMS require magnets and coils to be assembled, the assembly process is more complex, and the size is often larger than that of electrostatic or piezoelectric MEMS. They also consume more energy, so they may not be suitable for small applications that require battery operation for longer periods of time.
These types of MEMS each have different operating mechanisms and areas of strength. By using these MEMS appropriately according to their applications and purposes, many of the devices around us become more convenient and high-performance.